Decimals - Revision Notes
CBSE Class 6 Mathematics
Revision Notes
CHAPTER – 8
Decimals
- To understand the parts of one whole (i.e. a unit) we represent a unit by a block. One block divided into 10 equal parts means each part is (one-tenth) of a unit. It can be written as 0.1 in decimal notation. The dot represents the decimal point and it comes between the units place and the tenths place.
- Every fraction with denominator 10 can be written in decimal notation and vice-versa.
- One block divided into 100 equal parts means each part is (one-hundredth) of a unit. It can be written as 0.01 in decimal notation.
- Every fraction with denominator 100 can be written in decimal notation and vice-versa.
- In the place value table, as we go from left to the right, the multiplying factor becomes
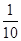
 of the previous factor.
of the previous factor. - Fractions as Decimals: Fractions can be converted into decimals by writing them in the form with denominators 10, 100 and so on. Example: =0.7
- Decimals as Fractions: Decimals can be converted into fractions by removing their decimal points and writing 10, 100, etc. in the denominators, depending upon the number of decimal places in the decimals. Examples: 0.9 =
- Addition of Decimals: Decimals can be added by writing them with equal number of decimals places. Example: add 0.005, 6.5 snd 20.04.
Solution: Convert the given decimals as 0.005, 6.500 and 20.040.
0.005 + 6.500 + 20.040 = 26.545 - Subtraction of Decimals: Decimals can be subtracted by writing them with equal number of decimal places.
Example: Subtract the given decimals as 5.674 and 12.500
12.500 – 5.674 = 6.826 - Comparing Decimals: Decimals numbers can be compared using the idea of place value: Example: 45.32 or 35.69
The given decimals have distinct whole number part, so we compare whole number part only. The whole number part of 45.32 is greater than 35.69. Therefore, 45.32>35.69. - Using Decimals: Many daily life problems can be solved by converting different units of measurements such as money, length, weight, etc. in the decimal form.
- Money:
100 paise = 1 Rupee
1 paise = 1/100 Rupee = 0.01 Rs.
5 paise = 5/100 Rs. = 0.05 Rs.
105 paise = 1 Rs. + 5 paise = 1.05 Rs.
7 Rs. 8 paise = 7 Rs. + 0.08 Rs = 7.08 Rs.
7 Rs. 80 paise = 7 Rs. + 0.80 Rs. = 7.80 Rs. - Length:
10 mm = 1 cm
1mm = 1/10 cm = 0.1 cm
100 cm = 1 m
1 cm = 1/100 m = 0.01 m
1000 m = 1 km
1 m = 1/1000 km = 0.001 km - Weight:
1000 g = 1 kg
1 g = 1/1000 kg = 0.001 kg
25 g = 25/1000 kg = 0.025 kg
