Air - Solutions
CBSE Class–VII Social Science
NCERT Solutions
Geography Chapter 4
Air
Q1. Answer the following questions.
- What is atmosphere?
- Which two gases make the bulk of atmosphere?
- Which gas creates a greenhouse effect in the atmosphere?
- What is weather?
- Name three types of rainfall.
- What is air pressure?
Answers:
- A huge blanket of air that surrounds our earth is called atmosphere. All living beings on this earth depend on the atmosphere for their survival. It provides us with the air we breathe and protects us from the harmful effects of the suns rays. Without this blanket of protection, we would be baked alive by the heat of the sun during the day and get frozen during the night. So it is this mass of air that has made the temperature on the earth live able.
The atmosphere has the following layers :- Troposphere.
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere
- Exosphere
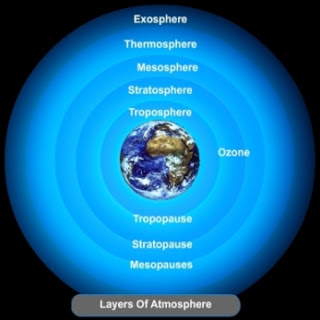
Our Atmosphere and its Layers - (a) Nitrogen (b) Oxygen. Nitrogen is the most plentiful gas in the air. When we inhale, we take some amount of nitrogen into our lungs and exhale it. But plants too need nitrogen for their survival and cannot take it directly from the atmosphere. Bacteria in the soil take nitrogen from the air and change its form so that plants can use it. Oxygen is the second most plentiful gas in the atmosphere. Humans and animals take oxygen from the air as they breathe. Green plants produce oxygen during photosynthesis.
- Carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is used by green plants to prepare food Whereas humans and animals release carbon dioxide. This perfect balance is being upset by the burning of fuels which add billions of tons of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere each year. This increased volume of carbon dioxide is affecting the earth's weather and climate.
- Weather is the hour-to-hour, day to day conditions of the atmosphere. It can be described as hot, humid, cold, breezy and pleasant.
- The three types of rainfall are (a) The conventional rainfall
(b) The orographic rainfall
(c)The cyclonic rainfall. - Air pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth's surface. As we go up the layers of the atmosphere, the pressure falls rapidly. The air pressure is highest at sea level and decreases with height. The air always moves from high-pressure areas to low-pressure areas.
Q2.Tick the correct answer:
- Which of the following gases protects us from harmful sun rays?
(a) Carbon dioxide (b) Nitrogen (c) Ozone.
Ans: (c) Ozone gas protects us from the harmful sun rays. - The most important layer of the atmosphere is.
(a) Troposphere (b)Thermosphere. (c) Mesosphere
Ans: (a) Troposphere is the most important layer of the atmosphere. - Which of the following layers of an atmosphere free from clouds?
(a) Troposphere (b) Stratosphere (c) Mesosphere
Ans: (b) Stratosphere layer is free from the atmosphere. - As we go up the layers of the atmosphere, the pressure
(a) Increases. (b) Decreases. (c) Remain the same
Ans: (b) As we go up the layers of the atmosphere, the pressure decreases - When precipitation comes down to the earth in liquid form, it is called:
(a) Cloud (b) Rain (c) Snow
Ans: (b) When precipitation comes down to the earth in liquid form, it is called rain.
Q3. Match the following:
| 1 | Tradewinds | (a) | Seasonal |
| 2 | Loo | (b) | Horizontal movement of air |
| 3 | Monsoon | (c) | Permanent wind |
| 4 | Wind | (d) | Local wind |
Ans:
| 1 | Tradewinds | (c) | Permanent wind |
| 2 | Loo | (d) | Local wind |
| 3 | Monsoon | (a) | Seasonal |
| 4 | Wind | (b) | Horizontal movement of air |
Q4. Give reasons.
- Wet clothes take a longer time to dry on a humid day?
Ans. On a humid day, the air has greater moisture. Hence, it is not able to carry the water vapor and so, wet clothes take a longer time to dry on a humid day. Wet clothes take longer time to dry on a humid day because the air has a lot of water vapour and so it can't accommodate the water vapour created by the wet clothes. So, the water remains, in the clothes for a longer time. - Amount of insolation decreases from the equator towards poles?
Ans: Insolation refers to the incoming solar power intercepted by the earth. Sunlight falls almost vertically on the equator, whereas it falls at some angles on the poles. So the amount of insolation decreases from the equator towards poles. From equator towards poles insolation comes through slanting rays. These slanting rays come on earth passing longer distance through the atmosphere. More heat is consumed in the space and atmosphere. It is because of these reasons that the amount of insolation decreases from the equator towards poles.
Q5. For fun.
(i). Solve this crossword puzzle with the help of given clues(on page no.28):
Ans:
| H | C | ||||||||||||||||||
| U | L | ||||||||||||||||||
| L | M | O | W | ||||||||||||||||
| R | O | I | U | P | E | E | P | A | L | ||||||||||
| C | A | R | B | O | N | D | I | O | X | I | D | E | A | T | |||||
| I | A | I | N | T | M | ||||||||||||||
| N | R | T | S | H | O | ||||||||||||||
| O | Y | E | X | O | S | P | H | E | R | E | S | ||||||||
| M | L | R | P | ||||||||||||||||
| E | A | I | R | F | H | ||||||||||||||
| T | T | O | X | Y | G | E | N | ||||||||||||
| N | E | E | M | W | I | N | D | G | R | ||||||||||
| R | O | E | |||||||||||||||||
| O | Z | O | N | E | |||||||||||||||
| C | Y | C | L | O | N | E |
(ii) Make a weather calendar for one week. Use pictures or symbols to show different types of weather. You can use more than one symbol in a day, if the weather changes. For example, the sun comes out when the rain stops. An example is given below:
Answer.
| Day | Symbol of Weather Conditions | Weather Conditions |
| Sunday |  | Sunny day |
| Monday |  | Cloudy day |
| Tuesday |  | Rainy day |
| Wednesday |  | Snowfall. |
| Thursday |  | Hail Storm. |
| Friday |  | Tropical-Storm |
| Saturday |  | Thunder Shower |
