Practical Geometry - Worksheets
CBSE Worksheet-1
CLASS –VII Mathematics (Practical Geometry)
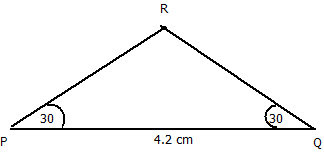
- Construct an isosceles triangle PQR where the non-equal side PQ = 4.2 cm and base angles are 30° each.
- If ABC exactly coincides with PQR then the triangles are________.
- In ABC, BC = CA. Which of its two angles are equal?
- If AB = QP, AC = QR, BC = PR, then ABC QPR, state the congruence criterion involved here.
- State true or false: The total measure of all the three angles of a triangle is 360°.
- If we have PQ = 5 cm, PQR= 115° and QRP = 30°, can we construct a PQR with these measurements?
- Construct a LMN, in which MN = 6cm, ML= 4.5 cm and M = 30°.
- Construct a right triangle PQR in which Q = 90°, PR = 6 cm and QR = 4 cm.
CBSE Worksheet-1
CLASS –VII Mathematics (Practical Geometry)
Answer key
- congruent.
Explanation:
If three sides and three angles of one triangle are equal to three sides and three angles of second triangle then the two triangles are said to be congruent. - A = B.
Explanation:
In an isosceles triangle, the angles opposite to equal sides are equal.
In ABC, the angle opposite to side BC is A and the angle opposite to side CA is B.
Hence, if BC = CA, then A = B. - SSS.
Explanation:
If three sides of a triangle are equal to three corresponding sides of another triangle, then the two triangles are said to be congruent according to SSS congruency criterion.
Given, in ABC and QPR,
AB = QP, AC = QR, BC= PR
Therefore, ABC QPR , by SSS congruency criterion. - False.
Explanation:
According to angle sum property of a triangle, sum of 3 angles of a triangle should be 180°. - Yes.
Explanation:
Given, in PQR, PQ = 5 cm, PQR= 115° and QRP = 30°
We can locate point R, by constructing the third QPR = 35° [180°- (115° + 30°)] from the point P, which meets PQR at R
