Pastoralists in the Modern World - Test Papers
CBSE TEST PAPER-01
Class –IX Social Science (Pastoralists in the Modern World)
General Instruction:
- All Questions are Compulsory.
- Question No. 1 to 4 carries one mark each.
- Question No. 5 and 10 carry three marks each.
- Question No. 11 and 12 carry five marks each.
- In which state Gujjar Bakarwals live?
- What is the group of several Gujjar households for journey called?
- Name the area where Gujjar enters the Kashmir Valley?
- Which community in Himachal Pradesh had a cycle of seasonal movement?
- Which conditions are responsible for the death of pastoral animals in the semi-arid regions of South Africa?
- Who are nomad pastoralists?
- How are pastoralists important in India?
- Write any three points related to the activities of Dhangars of Maharashtra?
- What are factors that affect the pastoral movement in plains?
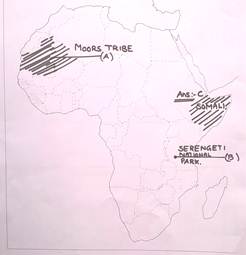
- Two features A and B are marked on the given political map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the map
- A famous tribe that lived in this area of North-west Africa
- A National Park
- On the same political map shade the appropriate area
- A place where Somali African tribe lived
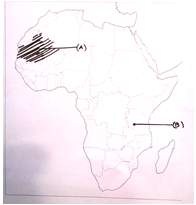
- Two features A and B are marked on the given political map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the map
- Explain the traditional authorities of the Elders and Warriors of the Massai Society?
- Who were nomads and what did they do?
CBSE TEST PAPER-01
Class –IX Social Science (Pastoralists in the Modern World)
[ANSWERS]
- Gujjar Bakarwals live in Jammu and Kashmir.
- The group of Gujjar households for the journey is called Kafila.
- Gujjar enters the Kashmir Valley near Pir Panjal Passes.
- Gaddis community in Himachal Pradesh had a cycle of seasonal movement.
- Following conditions are responsible for the death of pastoral animals in the semi-arid regions of South Africa
- Extremely hot and dry conditions
- Scanty rainfall
- Drought conditions are common in this semi-arid land of equatorial heat.
- During such times pastoral animals die in large numbers
- Nomad pastoralists are the people who move from one place to another place for their livelihood.
- They move with their herds of camels, cattle, sheep and goat.
- Estimated 30–40 million nomadic pastoralists worldwide, most are found in central Asia and the Sahel region of West Africa.
- Increasing numbers of stock may lead to overgrazing of the area and desertification if lands are not allowed to fully recover between one grazing period and the next.
- Increased enclosure and fencing of land have reduced the amount of land available for this practice.
- Pastoralists help in the maintenance of ecological balance.
- Pastoralists keep a large number of cattle wealth which is very helpful for the social economic development of the country.
- Pastoralists help in forest management.
- They also provide manure to the fields.
- Dhangars are one of the Nomadic pastoralists living in India. They live in the central plateau of Maharashtra during monsoon season.
- Most of them were shepherds, some were blanket weavers, and still other were buffalo herders.
- By October the Dhangars harvested their bajra and started on their move west.Dhangar flocks manured the fields and fed on the stubble.
- Following factors that affect the pastoral movement
- The movement of the pastoralists is affected by the availability of pastures, harvested fields, and water.
- When pastures are exhausted or are unusable due to excessive grazing in one place they move their herds to new areas.
- They move according to the time of advancing monsoon and retreating monsoon.
- In the dry season, they move towards the main area and return back at the arrival of monsoon.
- In pre-colonial times Massai society was divided into two social categories-elders and warriors.
- The elders formed the ruling group and met in periodic councils to decide on the affairs of the community and settle disputes.
- The warriors consisted of younger people, mainly responsible for the protection of the tribes.
- They defended the community and organized cattle raids. Raiding was important in a society where cattle were wealth.
- It is through raids that the power of different pastoral groups asserted and participating in wars. They, however, were subjected to the authority of the elders.
- Nomads are people who do not live in one place but move from one area to another to earn their living.
- They move with their herds of goats, sheep, camels, and buffalos.
- They do so to cope with the changing seasons to collect food for them and fodder for their pet animals.
- The sell milk, milk products, and animals and obtain necessary things.
- Raikas, Banjaras, and Gujjars are the examples of some nomadic communities.
