Natural Vegetation and Wild Life - Test Papers
CBSE TEST PAPER-01
Class –IX Social Science (Natural Vegetation and Wild Life)
General Instruction:
- All Questions are Compulsory.
- Question No. 1 to 4 carry one mark each.
- Question No. 5 and 10 carry three marks each.
- Question No. 11 and 12 carry 5 marks each.
- In which type of forests the roots of the plants are merged under water?
- Which famous animal is found in the tidal forest?
- Write one use of Sarpagandha.
- In which regions the mangrove forests found?
- Can you list out the range of animals survive in extreme cold of the Himalayan Harbour?
- Distinguish between reforestation and Afforestation.
- How do human beings influence the ecology of a region? Mention any three points.
- How far it is correct to say that Rann of kachchh is one of the extraordinary sights of India? Explain.
- What are biosphere reserves? And what are their uses.
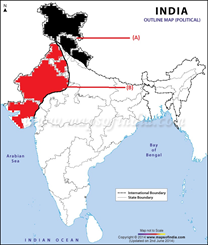
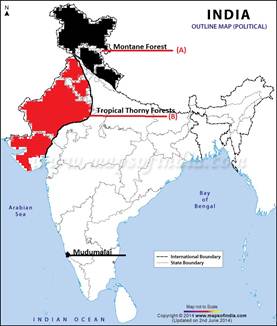
- Two features A and B are marked in the given political map of India. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the map .
- A Forest Type
- A Forest Type
- Madumalai- A wild life sanctuary
- Can you assess the significance of forests to enhance the quality of environment ? Justify the answer with suitable arguments.
- Describe the factors responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India.
CBSE TEST PAPER-01
Class –IX Social Science (Natural Vegetation and Wild Life)
[ANSWERS]
- Mangrove Forest type of forests the roots of the plants are merged under water.
- Royal Bengal Tiger is found in the tidal forest.
- Sarpagandha is used to treat blood pressure.
- Mangrove forests are found in the delta region of Ganga, the Mahanadi, and the Krishna.
- Hardy a range of animals survive in extreme cold of the Himalayan harbour.
- The freezing high altitudes of Ladakh are a home to Yak, the shaggy horned wild ox weighing around tones.
- The Tibetan antelope, the pharal (blue sheep), wild sheep are found here.
- The kiang-the Tibetan wild ass is also found in this region.
- The ibex, bear, snow-leopard and very rare red Panda are found in certain pockets.
Reforestation Afforestation 1. It is practiced in areas where forests have been destroyed. 1. New forests are planted in the new areas. 2. Two saplings are planted to replace every fallen tree. 2. One sapling is planted to get one tree. 3. It is practiced to avoid the evils of shifting agriculture. 3. It is practiced to bring more area under forests. - Human beings are an integral part of ecosystem.
- They utilize the vegetation and wildlife. The greed of human beings leads to over-utilization of these resources.
- They create ecological imbalance like cutting of trees and the killing of animals.
- They are also responsible for extinctions of some species of plants and animals
- Some of the wetlands of India are popular with migratory birds, during winter . Birds, such as Siberian Crane come in large number. One such place favourable with birds is the Rann of Kachchh. At this place where the desert merges with the sea, flamingo with their brilliant, pink plumage, come in thousands to built nest mounds from the salty mud and raise their young ones. Due to this reason environmentalists consider this place an extraordinary sight in the country. It is also a rich natural heritage of our country.
- the protected areas reserved for the conservation of endangered species of flora and fauna in their natural habitat is called a biosphere reserves. Following are the uses of biosphere reserves:
- Endangered species of animals and plants are protected.
- These rare plants and animals are transmitted to the future generations in all their natural glory.
- The surrounding areas are reserved for research work for the betterment of flora and fauna.
- Forests play a significant role to enhance the quality of environment as they are renewable resources.
- Forests control soil erosion, modify local climate regulate stream flow, support a variety of life , provide livelihood for many communities and raw materials to many industries
- Forests offer panoramic or scenic view of recreation.
- It controls temperature and causes rainfall.
- It provides humus to the soil and enhances the fertility of soil.
- Forests provide shelter to wild life.
- Land: The nature of land influences the type of vegetation. The fertile land is generally devoted to agriculture. The undulating and rough terrains are the areas where grassland and woodlands develops and give shelter to a variety of wildlife.
- Soil: different types of soils provide basis for different types of vegetation. The sandy soils the desert support cactus and thorny bushes while wet, marshy, deltaic soils support mangroves and deltaic vegetation. The hill slopes with some depth of soil have conical trees.
- Temperature: on the slopes of the Himalayas and the hills of the peninsula above the height of 915 meters, the fall in temperature affects the types of vegetation and its growth and it changes it from tropical to sub-tropical temperate and alpine vegetations.
- Photoperiod: The variation in duration of sunlight at different places is due to differences in latitude, altitude, season and duration of the day. Due to longer duration of sunlight, trees grow faster in summer.
- Precipitation: Areas of heavy rainfall have more dense vegetation as compared to other areas of less rainfall.
