Improvement in Food Resources - Solutions
CBSE class IX Science
NCERT Solutions
Chapter 15
Improvement in Food Resources
(Page No. 204)
1. What do we get from cereals, pulses, fruits and vegetables?
Ans. We get carbohydrates from cereals, proteins from pulses, vitamins and minerals from fruits and vegetables.
(Page No. 205)
1. How do biotic and abiotic factors affect crop production?
Ans. Crop production can go down due to biotic (diseases due to infection by vriuses or fungi, insects) and abiotic (drought, salinity,water logging, heat,cold and frost) stresses under different situations.
2. What are the desirable agronomic characteristics for crop improvements?
Ans. The desirable agronomic characteristics for crop improvements are as follows:
- For cereal crops desirable characteristic is dwarfness since such plants will utilise less amount of nutrients.
- For fodder crops desirable characteristics are tallness and profuse branching so that we can obtain more amount of leaves for feeding our animals.
(Page No. 206)
1. What are macro-nutrients and why are they called macronutrients?
Ans. There are sixteen nutrients which are essential for plants. Among these thirteen nutrients, six are required in large quantities and are therefore called macronutrients.
Macronutrients: nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulphur.
2. How do plants get nutrients?
Ans. Nutrients are supplied to plants by air, water and soil.
(Page No. 207)
1. Compare the use of manure and fertilizers in maintaining soil fertility.
Ans. Manure is prepared by the decomposition of animal excreta and plant waste so contains large quantities of organic matter and also supplies small quantities of nutrients to the soil that improves soil fertility.
Fertilizers are commercially produced in factories to supply nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium that ensures soil fertility in terms of proper dose, time, and observing pre and post-application precautions.
(Page No. 208)
1. Which of the following conditions will give the most benefits? Why?
(a) Farmers use high-quality seeds, do not adopt irrigation or use fertilizers.
(b) Farmers use ordinary seeds, adopt irrigation and use fertilizer.
(c) Farmers use quality seeds, adopt irrigation, use fertilizer and use crop protection measures.
Ans. (c) Farmers use quality seeds, adopt irrigation, use fertilizer and use crop protection measures.
(i) The use of good quality seeds increases the total crop production. If a farmer is using good quality seeds, then a majority of seeds will germinate properly, and will grow into a healthy plant.
(ii) Proper irrigation methods improve the water availability to crops.
(iii) Fertilizers ensure healthy growth and development in plants by providing the essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc.
(iv) Crop protection measures include various methods to control weeds, pests, and infectious agents.
If all these necessary measures are taken by a farmer, then the overall production of crops will increase.
(Page No. 209)
1. Why should preventive measures and biological control methods be preferred for protecting crops?
Ans. Prevention is better than cure so it is true for plants also. Preventive measures (such as use of resistant varieties of crops) and biological control methods should be preferred for protection of crops because they are ecologically safe, target specific and harmless to other life forms.
2. What factors may be responsible for losses of grains during storage?
Ans. Factors that may be responsible for losses of grains during storage are:
Abiotic factors: Unfavourable conditions of humidity and temperature.
Biotic factors: Insects, rodents, bacteria, fungi etc that feed on grains.
(Page No. 210)
1. Which method is commonly used for improving cattle breeds and why?
Ans. The method of cross breeding is commonly used for improving cattle breeds.
For example in milch animals exotic or foreign breeds (for example, Jersey, Brown Swiss) are selected for long lactation periods, while local breeds (for example, Red Sindhi, Sahiwal) show excellent resistance to diseases. The two can be cross-bred to get animals with both the desired qualities.
(Page No. 211)
1. Discuss the implications of the following statement:
“It is interesting to note that poultry is India’s most efficient converter of low fibre food stuff (which is unfit for human consumption) into highly nutritious animal protein food.”
Ans. Under poultry the birds kept are fed on agricultural waste material and broken grains etc which are not useful for humans but those birds consuming such waste provide us with eggs and meat which is highly nutritious animal protein food hence the statement made is quite appropriate.
1. What management practices are common in dairy and poultry farming?
Ans. The management practices that are common in dairy and poultry farming are:
• Proper feeding
• Proper cleaning and shelter facilities
• Protection from unfavorable climatic conditions and diseases.
• Protection from pests.
2. What are the differences between broilers and layers and in their management?
Ans.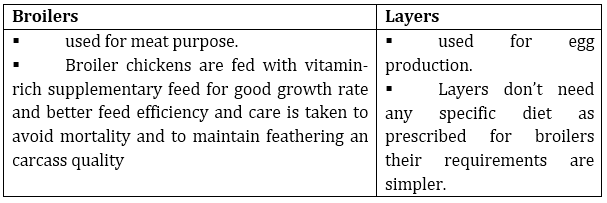
Other than above differences housing, nutritional and environmental requirements of broilers are somewhat different from those of egg layers.
(Page No. 215)
1. How are fish obtained?
Ans. There are two ways of obtaining fish. They can be obtained by:
a) Capture fishing: It is the way of obtaining fish from their natural resources (rivers, lakes, oceans).
b) Culture fishery: It is also known as fish farming where selected fishes are reared and bred.
2. What are the advantages of composite fish culture?
Ans. Compositefish culture has following advantages:
• Both local and imported fish species can be used in such systems.
• Due to non-competitive nature of selected fishes food available in all the parts of the water reservoir is used.
• Increases the fish yield from the water reservoir (intensive fish farming).
1. What are the desirable characters of bee varieties suitable for honey production?
Ans. The desirable characters of bee varieties suitable for honey production are:
• high honey collection capacity.
• they must sting less.
• They should stay in a given beehive for long periods, and breed very well.
2. What is pasturage and how is it related to honey production?
Ans. Pasturage refers to the flowers available to the bees for nectar and pollen collection. The value or quality of honey depends upon the pasturage. Along with this the kind of flowers available will determine the taste and quality of the honey.
(Chapter – end)
1. Explain any one method of crop production which ensures high yield.
Ans. To ensure high yield various cropping patterns can be very useful. The cropping patterns to be mentioned here are:
- mixed cropping
- inter cropping
- crop rotation
Mixed cropping is growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same piece of land, for example, wheat + gram, or wheat +mustard, or groundnut + sunflower. This reduces risk and gives some insurance against failure of one of the crops.
Inter-cropping is growing two or more crops simultaneously in the same field in a definite pattern (as shown below). The crops are selected such that their nutrient requirements are different. This ensures maximum utilisation of the nutrients supplied, and also prevents pests and diseases from spreading to all the plants belonging to one crop in a field for example, soyabean + maize, or finger millet (bajra) + cowpea (lobia).
Crop rotation is growing of different crops on a piece of land in a pre-planned succession. Depending upon the duration, crop rotation is done for different crop combinations. The availability of moisture and irrigation facilities decide the choice of the crop to be cultivated after one harvest. If crop rotation is done properly then two or three crops can be grown in a year with good harvests. For example - Maize + Mustard are grown in one year rotation and Maize + Potato + Sugarcane + Peas are grown in two years rotation.
2. Why are manure and fertilizers used in fields?
Ans. Manure helps in enriching soil with nutrients and organic matter and increasing soil fertility. The bulk of organic matter in manure helps in improving the soil structure.
Fertilizers are used to ensure good vegetative growth (leaves, branches and flowers), giving rise to healthy plants by providing specific nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
3. What are the advantages of inter-cropping and crop rotation?
Ans.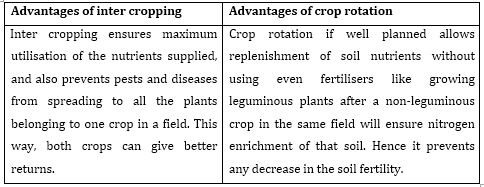
4. What is genetic manipulation? How is it useful in agricultural practices?
Ans. Plant breeding or hybridisation method that involves crossing two different plant varieties to obtain a new and better variety is called genetic manipulation.
In agricultural practices to reduce the application of insecticides and fungicides or even fertilizers such varieties are being prepared that are:
- high yielding
- pest resistant
- resistant to environmental stress
- doesn’t need fertilizers for good growth
All these features help not only to improve quality and quantity of products but also reduces chances of environmental pollution.
5. How do storage grain losses occur?
Ans. There are various biotic and abiotic factors responsible for the storage grain losses:
• Biotic factors: Insects, rodents, bacteria, fungi etc that feed on grains.
• Abiotic factors: Unfavourable conditions of humidity and temperature.
Thus, combination of biotic and abiotic factors causes infestation of insects, degradation in quality, loss in weight, poor germinability, discolouration of produce, poor marketability and economic loss.
6. How do good animal husbandry practices benefit farmers?
Ans. Animal husbandry is the scientific management of animal livestock. It includes various aspects such as feeding, breeding and disease control.
As the population increases and so do living standards increase, the demand for milk, eggs and meat is also going up. Also, the growing awareness of the need for proper treatment of livestock has brought new limitations in livestock farming. Thus, livestock production also needs to be improved. This improvement can be brought about by good animal husbandry practices like providing good food and preventing diseases in the cattles that will benefit farmers to obtain better quality and quantity products.
7. What are the benefits of cattle farming?
Ans. Cattle farming has dual benefits:
(i) Draught animals for farm labour (males)i.e. for agricultural work such as tilling, irrigation and carting.
(ii) Milch animals (dairy animals) which are milk producing females.
8. For increasing production, what is common in poultry, fisheries and bee-keeping?
Ans. For increasing production, steps that are common in poultry, fisheries and bee-keeping are as follows:
Variety improvement, housing, rearing, sanitation, disease control and marketing.
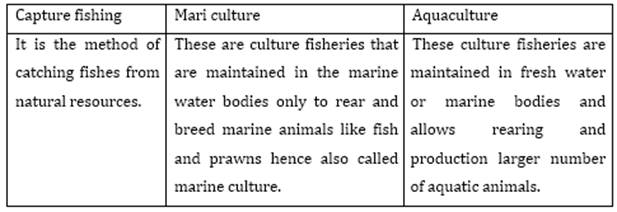
9. How do you differentiate between capture fishing, mariculture and aquaculture?
Ans.