Herons Formula - Test Papers
CBSE Test Paper 01
CH-12 Herons Formula
- The perimeter and area of a triangle whose sides are of lengths 3 cm, 4 cm and 5 cm respectively are
- 12 cm, 6
- 12 cm, 12
- 6 cm, 6
- 6 cm, 12
- Each equal side of an isosceles triangle is 13 cm and its base is 24 cm Area of the triangle is :
- 60
- An isosceles right triangle has area 8 . The length of its hypotenuse is
- cm
- cm
- cm
- cm
- If side of a scalene is doubled then area would be increased by
- 200%
- 25
- 50
- 300
- One of the diagonals of a rhombus is 12cm and area is 96 sq cm. the perimeter of the rhombus is
- 72 cm
- 40 cm
- Fill in the blanks: The area of a triangle of base 35 cm is 420 cm2, then its altitude is ________ cm.
- Fill in the blanks: The altitude of an equilateral triangle ABC is ________.
- The base and the corresponding altitude of a parallelogram are 10 cm and 7 cm, respectively. Find its area.
- How many times area is changed, when sides of a triangle are doubled.
- Find the area of a triangle whose sides are 9 cm, 12 cm and 15 cm.
- An isosceles triangle has perimeter 30 cm and each of the equal sides is 12 cm. Find the area of the triangle.
- The base of a right-angled triangle measures 4 cm and its hypotenuse measures 5 cm. Find the area of the triangle.
- The perimeter of a triangle is 300 m. If its sides are in the ratio 3 : 5 : 7 . Find the area of the triangle.
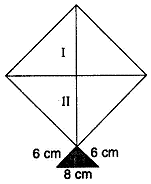
- A kite in the shape of a square with diagonal 32 cm and an isosceles triangle of base 8 cm and side 6 cm each is to be made of three different shades as shown in a figure. How much paper of each shade has been used in it? (Use = 2.24)
- Two parallel side of a trapezium are 60 cm and 77 cm and other sides are 25 cm and 26 cm. Find the area of the trapezium.
CBSE Test Paper 01
CH-12 Herons Formula
Solution
- (a) 12 cm, 6
Explanation: Perimeter of triangle = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 cmNow, s = cm
Area =
=
= 6 sq cm
- (c) 60
Explanation:
s = = 25 cm
Area of triangle =
=
=
= 60 sq. cm
- (a) cm
Explanation:Area of isosceles triangle = x Base x Height
Since in an isosceles triangle, Base and Height are equal.
=> 8 = x Base x Base
=> Base = Height = 4 cm
Hypotenuse = = cm
- (d) 300
Explanation:Area of triangle with sides a, b, c (A) =
New sides are 2a, 2b and 2c
Then
=> s' = 2s .............(i)
New area =
=
=
= 4A
Increased area = 4A - A = 3A
% of increased area = = 300%
- (c) 40 cm
Explanation:d2 =
=
=16 cm
length of side of rhombus = = 10 cm
perimeter of rhombus = 4 x side
= 4 x 10 = 40 cm
24
The base of parallelogram =10 cm and the corresponding altitude = 7 cm.
Area of parallelogram = Base Corresponding altitude
= 10 7 = 70 cm2.Area of triangle = × base × height = × b × h
If new base B = 2b and height H = 2h
New area of triangle = × B × H = × 2b × 2h =4( × b × h) = 4 (area of triangle)
So doubling the sides leads to 4 times the area.Let a = 9 cm, b = 12 cm and c = 15 cm
Since, 2s = a + b + c
s = (a + b + c)
= (9 + 12 + 15)
= (36) = 18 cm
Now, area of triangle =
=
=
= 54 cm2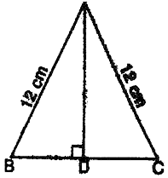
a = 12 cm, b = 12 cm
Perimeter = 30 cm
a + b + c = 30
⇒ 12 + 12 + c = 30
⇒ 24 + c = 30
⇒ c = 30 – 24
⇒ c = 6 cm
s = cm = 15 cm
∴ Area of the triangle
cm2Given: base of a right-angled triangle = 4 cm and hypotenuse = 5 cm.
In right-angled triangle ABC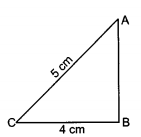
AB2 + BC2 = AC2 (By Pythagoras Theorem)
AB2 + 42 = 52
AB2 = 25 - 16 = 9
AB = 3 cm
Area of
Hence area of given right-angled triangle is 6 cm2.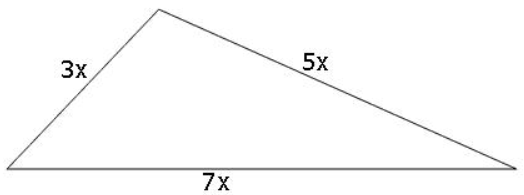
Suppose that the sides in metres are 3x, 5x and 7x.
Then, we know that 3x + 5x + 7x = 300 (Perimeter of the triangle)
Therefore, 15x = 300, which gives x = 20.
So the sides of the triangles are 3 20 m, 5 20 m and 7 20 m
i.e., 60m, 100m and 140m.
We have s = = 150 m
and area will be =
=
= 1500 m2Here ABCD be the square and CEF be an isosceles triangle.
Let the diagonals bisect each other at O.
Then,
AO = 32 cm
= 16 cm
Area of shaded portion I =
= 256 sq cm
Similarly, Area of shaded portion II =
= 256 sq cm
And, for triangle
base, a = 8 cm
and side, b = 6 cm
Area of portion III =
= 17.92 sq cm
Thus, the papers of three shades required are 256 sq cm, 256 sq cm and 17.92 sq cm.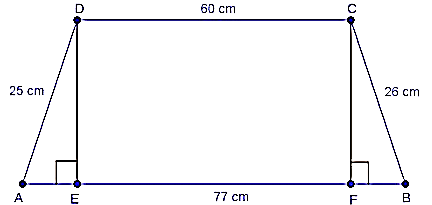
Given that,
AB = 77 cm, CD = 60 cm, BC = 26 cm and AD = 25 cm
Now, DE AB and CF AB is drawn.
EF = DC = 60 cm
Let AE = x
BF = 77 - 60 - x = (17 - x)
In ADE, DE2 = AD2 - AE2 [pythagoras theorem]
= 252 - x2
And BCF, CF2 = BC2 - BF2 [pythagoras theorem]
= 262 - (17 - x)2
But DE = CF DE2 = CF2
25 - x2 = 262 - (17 - x)2
252 - x2 = 262 - (289 + x2 - 34x) [ (a - b)2 = a2 + b2 - 2ab]
625 - x2 = 676 - 289 - x2 + 34x
34x = 238
x = 7
DE = = = = 24 cm
Area of trapezium = (sum of parallel sides) height
= (60 + 77) 24 = 1644 cm2
