Forest Society and Colonialism - Test Papers
CBSE TEST PAPER-01
Class – IX Social Science (Forest Society and Colonialism)
General Instruction:
- All Questions are Compulsory.
- Question No. 1 to 4 carry one mark each.
- Question No. 5 to 10 carry three marks each.
- Question No. 11 and 12 carry five marks each.
- Who were the people who move from one place to the other to herd their sheep, goat and cattle?
- How much area of forest cover in the world was cleared for industrial uses, cultivation, pastures and firewood, between the years of 1700 to 1995?
- How much India’s landmass had been under cultivation in 1600?
- How much sleepers were required for each mile railway track?
- Explain any three reasons for the rapid expansion of cultivation during colonial rule.
- Write some products which we get from the forests.
- What are the main reasons for rapid disappearance of forests?
- Why it was necessary to bring more area under cultivation?
- Who was Richard Harding?
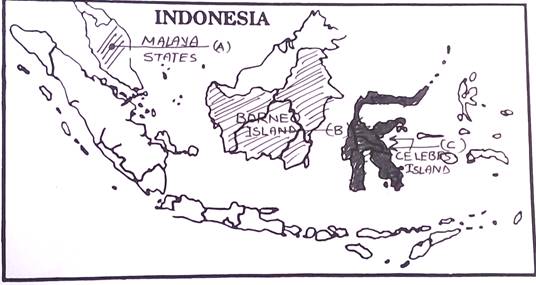
- On the given out line Map of Indonesia mark and show the following:
- Malaya States,
- Borneo Island,
- Celebes Island
- How forest products are useful for tribal people? Explain with examples.
- 'The Forest Acts meant severe hardship for villager across the country'. Elaborate the statement with suitable reasons.
CBSE TEST PAPER-01
Class – IX Social Science (Forest Society and Colonialism)
[ANSWERS]
- Pastoralists.
- 13.9 million square km forest cover in the world was cleared for industrial uses, cultivation, pastures and firewood, between the years of 1700 to 1995.
- About one-sixth of India’s landmass had been under cultivation in 1600.
- About 1760 to 2000 sleepers were required for each mile railway track.
- The 3 major reason behind the rapid expansion of cultivation during colonial rule are:
- The British directly encouraged the production of commercial crops like Jute, sugar, wheat and cotton.
- The demand for these crops increased in nineteenth-century Europe where foodgrains were needed to feed the growing urban population.
- raw materials were required for industrial production.
- Some products which we get from the forests are:
- Fruits and roots from forests.
- Forests provide us timber for manufacturing furniture.
- We get honey, gum, rubber, fodder etc from forests.
- The main reasons behind rapid disappearance of forests are:
- Forests were cleared to set up industries.
- More areas were required for agriculture to feed the growing population.
- Wood was required for fuel purpose.
- Colonial rule was also responsible for the disappearance of forests.
- It was necessary to bring more area under cultivation
- To meet the food-grain demand of the ever-growing population.
- The British encouraged the production of cash crops.
- The demand for cash crops as well as foodgrains increased due to urbanization.
- The British considered forests as unproductive. They wanted to get more land revenue. So, more area was brought under cultivation.
- Richard Harding was an American writer. He justified the land acquisition in an interesting manner. He said that it was better to keep the land under the colonial powers to improve it. He said that original people were not doing enough to improve the land. They never understood the value of the land. He termed the native of Central America as the semi-barbarians who could never understand the value of luxury and comforts.
- Forest products are useful for tribal people in many ways:
- In forest areas, people use forest products - roots, leaves, fruits and tubers - for many things.
- Fruits and tubers are nutritious to eat, especially during the monsoons before the harvest come in.
- Herbs are used for medicine, wood for agricultural implements like yokes and plough, bamboo makes excellent fences and is also used to make baskets and umbrellas.
- A dried scooped–out gourd can be used as a portable water bottle. Almost everything is available in the forest - even the leaves can be stitched together to make disposable plates and cups.
- Creepers can be used to make ropes, and the thorny bark of the silk cotton tree is used to grate vegetables. Oil for cooking and to light lamps can be pressed from the fruit of the Mahua tree.
- 'The Forest Acts meant severe hardship for villager across the country' as after the implementation of the act -
- All the everyday practices of the villagers like cutting wood for houses became illegal.
- The villagers were are not allowed to collect fruits and roots from the forests.
- Hunting and fishing became illegal.
- People were now forced to steal wood from the forests, if they were caught they were at the mercy of the forest guards who would took bribes from them.
- Women who collected fuel wood were especially worried.
- It was also common for police constable and forest guards to harass people by demanding free food from them.
