Ch20 India Transport - Test Papers
CBSE Test Paper 01
- Name the states with highest and lowest density of roads.
- Which means of transport is being used widely in India?
- Name the railway line that was constructed between Roha in Maharashtra and Mangalore in Karnataka.
- Explain the term ‘Golden Quadrilateral’.
- What are the major problems of the Indian railway?
- Explain any three features of National Waterway-3 of India.
- Which activity does transportation convey? Name three major modes of transportation.
- India is deemed to have one of the world's largest road network. Why?
- Discuss the growth and role of TV and radio in mass communication.
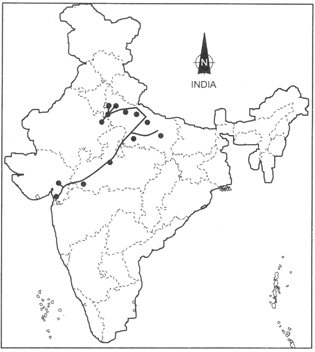
- What does the line given below in the political map of India indicate?
CBSE Test Paper 01
Ch-20 India Transport and Communication
Answer
- The density of road is high in most of the northern states and major southern states.
- It is low in the Himalayan region. North-eastern region, M.P and Rajasthan.
- Density of all roads varies from only 10 km in Jammu & Kashmir to 375 km in Kerala with the national average of 75 km.
Land transport is being used widely in India
Konkan railway line was constructed between Roha in Maharashtra and Mangalore in Karnataka.
Golden Quadrilateral is a 4 or 6 lane super-highway project undertaken by the National Highway Authority of India. It is a 5846 km long highway meant to connect India's four big metro cities of Delhi-Mumbai-Chennai-Kolkata.
The major problems of the Indian railway are:
- Heavy expenditure in railways development.
- In the areas of turbulent flow of river a big expenditure on the development.
- Swampy, flood areas are not fit for its development.
- The sand dunes in the desert are the main problems for development.
- Forest and Uneven Lands are the hurdles in the way of railway development.
- Highly affected by stricks, due to political interference and fog, etc.
- The National Waterway- 3 stretches from Kottapuram to Kollam. It is on a backwater.
- The total length of this National Waterway is 205 km and it is open on February 1, 1991.
- The specification of this waterways is that as it includes 168 km of west coast canal along with Champakara canal (23 km) and Udyogmandal canal (14 km).
Transport is included in tertiary activities. Under this, people and goods are taken from one place to another. There are three types of transport:
- Land transport- Roads, railways, ropeways, and pipelines.
- Water transport- Inland waterways, sea routes, and ocean routes.
- Air transport- National and International.
India has one of the largest road networks in the world because of the following reasons:
- The Road network of India is second largest road network in the World with total length of around 33.1 lakh kilometers.
- According to 2005 survey about 85 % of passenger and 70% of freight is carried using road network.
Radio:
- Radio broadcasting was started in India in 1923 by the Radio Club of Bombay.
- Since then, it gained immense popularity and changed the socio- cultural life of people.
- Government took mode of communication under its control in 1930 under the Indian Broadcasting System. It was changed to All India Radio in 1936 and to Akashwani in 1957 (TV).
Television:
- TV broadcasting has emerged as the most effective audio-visual medium for disseminating information and educating masses.
- Initially, the TV services were limited only to the national capital where it began in 1959. After 1972, several other centres became operational.
- In 1976, TV was delinked from All India Radio (AIR) and got a separate identity as Doordarshan (DD).
- After INSAT-IA (National Television-DDl) became operational. Common National Programme (CNP) was started for the entire network and its services were extended to the backward and remote rural areas.
Role of TV and Radio in mass communication:
- Variety of programmes related to information, education and entertainment is done via All India Radio.
- Special news bulletins at specific occasions like session of parliament and state legislatures are also broadcasted.
- For the purpose of advertisement for various products, TVs and Radios are used.
- For creating awareness on government policies and programmes these medium is useful.
- They act as a measure of public health by creating awareness about various diseases and their precautions.
- Weather forecasting information, important facts and figures reach to general public only through radio and TV.
The line given in the political map of India indicates the Hazira-Vijapur-Jagdishpur Pipeline
