Ch09 International Trade - Test Papers
CBSE Test Paper 01
What are regional trade blocs?
Name the international organisation dealing with the global rules of trade between nations.
Name the important entrepot port of Asia.
How is the favourable balance of trade an indicator of economic development of a country?
Define the word 'Port'? Write the classification of ports on the basis of their location.
On the basis of following table, answer the following questions:
World exports and imports (in millions of US $) Year 1955 1965 1975 1985 1995 2005 Total Merchandised Exports 95000 190000 877000 1954000 5162000 10393000 Total Merchandised Imports 99000 199000 912000 2015000 5292000 10753000 - What was total value of merchandised exports in 2005?
- What was the value of goods imported in 2005?
- What was the difference between exports and imports in 2005?
- Who is the biggest trading partner of India?
Explain with an example, how the stage of economic development and foreign investment become the basis of international trade.
Mention any six characteristics of Regional Trade Blocs of the world.
Explain the two types of international trade. Examine any three possible negative impacts of globalisation along with free trade in the world.
On the political map of world, mark and locate the member nations of OPEC.
CBSE Test Paper 01
Ch-9 International Trade
Answer
A regional trading bloc (RTB) is a co-operative union or group of countries within a specific geographical boundary. RTB protects its member nations within that region from imports from the non-members.The primary aim of trade block activities is to create a favorable economic framework for promotion of cross border trade among the member countries.
The international organisation dealing with the global rules of trade is World Trade Organisation (WTO).
Singapore is the important entrepot port of Asia.
A favourable balance of trade means that the value of exports is more than the value of imports. This means that the country is earning money by selling its goods which is an indicator of the economic development of a country.
Ports are the medium of trade between the two countries. It is that place on the coast where cargo in large quantity is received from oceanic routes and sent to the interior parts of the country.
Two types of Ports on the basis of location are:- Out-ports - deepwater port built away from the actual port.
- Inland port - located away from the coast and liked with the sea through a river or a canal.
- 10393000 millions US $
- 10753000 million US $
- 360000 millions US $
- USA
- Table shows that trade of primary products was dominant in the beginning of the last century. Later manufactured goods gained prominence and currently, though the manufacturing sector commands the bulk of the global trade, service sector which includes travel, transportation and other commercial services have been showing an upward trend. It also shows that the volume of imports and exports of the world merchandise has been growing consistently over the years.
In modern times, trade is the basis of the world's economic organisation and is related to the foreign policy of nations. The stage of economic development and foreign investment have become the basis of international trade due to following reasons:
- Size of Economic Development: The nature of trade changes with the change in the stage of economic development of countries. In developed economies, manufactured goods, machinery are traded for raw materials but in less developed economies, agro products are traded for industrial goods.
- Foreign Investment: Developing countries lack the capital which is required for the development of mining, oil drilling, heavy engineering, lumbering, and plantation agriculture. Foreign investment can boost trade in these countries. Like in India, foreign investment in service sectors has made India one of the leading service provider countries in the world.
The six characteristics of the ‘Regional Trade Blocs' of the world are as under:
- The main aim of the regional trade blocs is to enhance and encourage trade between countries with geographical proximity.
- To encourage the complementarities in trading items.
- The aim is to curb the restrictions on the trade of the developing world.
- The regional trading blocs mainly developed and promoted as the response to the failure of global organizations.
- These regional trading blocs have eliminated the trade tariffs of their own member nations to promote free trade.
- ASEAN, SAFTA, EU, OPEC are some examples of the regional trading blocs of the world.
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods and services across international borders or territories. There are two types of international trade:
- Bilateral Trade: It refers to the trade between the two countries. The two countries are specialised in certain commodities and hence, they enter into an agreement to trade specified commodities between them.
- Multilateral Trade: It is conducted with many trading countries. The same country can trade with a large number of other countries. The status of the Most Favoured Nation (MFN) can be granted by such country to some of the trading partners.
Three possible negative impacts of globalisation along with free trade in the world are as follows:
- It does not provide level playing field by imposing unfavourable conditions hence, retard the growth of trade for developing countries.
- Cheaper goods from foreign countries may harm the sale of domestic goods.
- The phenomena of dumping may be visible in the markets of developing countries.
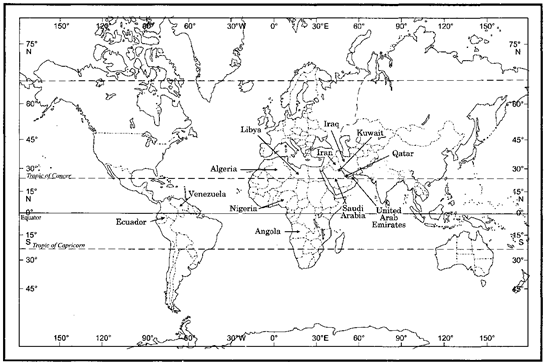
The current OPEC members are: Algeria, Angola, Ecuador, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, the Republic of the Congo, Saudi Arabia (the de facto leader), United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela. Indonesia is a former member.
