Ch05 Primary Activities - Test Papers
CBSE Test Paper 01
- What is nomadic herding?
- Write any two plantation crop.
- What do you mean by 'Factory Farming'?
- In which agriculture single crop specialization is one of the features?
- Explain two features of three crop seasons of India.
- What are the types of farming according to the farming organization?
- What do you mean by plantation agriculture?
- What is Plantation Agriculture? Why is it practised mainly in tropical and sub-tropical areas of the world?
- Explain the differences between mixed farming and dairy farming.
- Study the following map and on the basis of shaded areas, answer the following questions:-
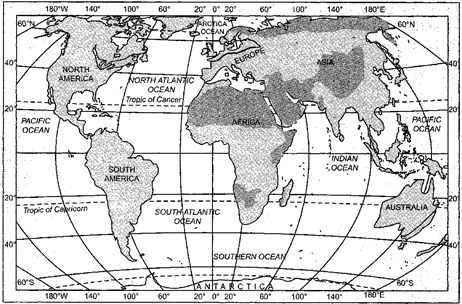
- Which economic activity is revealed by the shaded portion?
- What are the products of primary activities in this area?
- Which types of climatic conditions are present in this region?
CBSE Test Paper 01
Ch-5 Primary Activities
Answer
Nomadic herding is also called pastoral nomadism. It is basically a primitive subsistence activity in which herders depend upon animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools, and transport.
Two plantation crops are Coconut & Coffee.
Raising of livestock, particularly poultry and cattle rearing, with heavy capital and specialisation is called factory farming. OR A system of rearing livestock using highly intensive methods, by which poultry, pigs, or cattle are confined indoors under strictly controlled conditions.
Single crop specialization is one of the features of plantation agriculture.
The Indian cropping season is classified into three crop seasons in interiors and Northern parts of India: Rabi,Kharif and Jayad. Their features are as follows:
- Kharif crops are sown with South-west Monsoon in June-July and harvested in January. It includes crops like rice, cotton, jute, jawar, bajra, arhar and corn.
- Rabi crops are sown in October-November and harvested in March-April. It includes wheat, gram, mustard, etc.
- Jayad is a short term summer crop. These crops are sown after rabi crops. It includes water-melon, musk-melon, cucumber, vegetables and fodder, etc.
- Co-operative farming: Group of farmers voluntarily pool their land and resources and form co-operative society. It is practised in Denmark, Netherlands, Sweden, Italy, Belgium, In Denmark every farmer is a member of a Co-operative.
- Collective farming: It is based on social ownership of means of production and collective labour. It was adopted in U.S.S.R after the 1917 revolution. Farmers pool their resources like land, livestock, and labour in Collective farming.
It is a method of farming in which large estates or plantations are purchased and large capital investment is done along with providing for scientific and technical support and most modern methods of cultivation with specialisation in a single crop. It was introduced by the Europeans in colonies situated in the tropics. Plantation agriculture is a form of commercial farming where crops are grown for profit. Countries that have plantation agriculture usually experience tropical climate with high annual temperatures and receive high annual rainfall.
It is a special type of farming in which crops like tea, coffee, bananas and rubber etc. are grown in big estates by using modern techniques. Crops are grown for commercial purposes. This agriculture requires more investment. Reasons for plantation agriculture in tropical areas:
- Hot and humid climate
- Fertile soil
- Availability of cheap labour due to high density of population.
Mixed farming is a type of farming in which cultivation of crops and raising livestock goes hand in hand. Its main features are:
- This form of agriculture is found in the highly developed parts of the world, e.g. North-western Europe, Eastern North America, parts of Eurasia and the temperate latitudes of southern continents.
- Mixed farms are moderate in size.
- Equal emphasis is laid on crop cultivation and animal husbandry.
- Fodder crops are an important component of mixed farming.
- Crop rotation and intercropping play an important role in maintaining soil fertility.
- It is characterised by high capital expenditure on farm machinery and building, i extensive use of chemical fertilisers and green manures.
- The crops associated with it are wheat, barley, oats, rye, maize, fodder and root crops.
- Animals like cattle, sheep, pigs and poultry provide the main income along with crops.
Dairy Farming: Dairy farming is a type of agriculture in which major emphasis is on breeding and rearing milch cattle. Its main characteristics are given below which can prove that it is a modern occupation:
- It is highly capital intensive. Large investments are made on animal sheds, storage facilities for fodder, feeding and milching machines.
- Special emphasis is laid on cattle breeding, health care and veterinary services.
- It is also highly labour intensive as it involves painstaking care in feeding and milching.
- There is no off-season during the year.
- It is practised mainly near urban and industrial market.
- Dairy farming development depends on transportation, refrigeration, pasteurisation and other preservation processes.
- There are three main regions of commercial dairy farming:
- The largest is North-Western Europe.
- Second is Canada.
- The third belt includes South Eastern Australia, New Zealand and Tasmania.
- Nomadic herding
- Milk, meat, skin, wool and other animals products
- Tundra type of climatic conditions are found here.
