Business Environment - Revision Notes
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies
Revision Notes
CHAPTER – 3
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
Meaning of Business Environment:
Business environment refers to forces and institutions outside the firm with which its members must deal to achieve the organisational purposes. Here
• Forces = economical, social, political, technological etc
• Institutions = suppliers, customers, competitors etc
It includes all those constraints and forces external to a business within which it operates. therefore,
• The firm must be aware of these external forces and institutions and
• The firm must be nagged keeping in mind these forces and institutions so that the organisational objectives are achieved. .
Features of Business Environment
1. Totality of external forces: Business environment is the sum total of all the forces/factors external to a business firm.
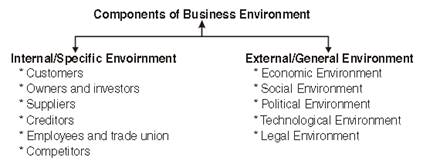
2. Specific and general forces: Business environment includes both specific and general forces. Specific forces include investors, competitors, customers etc. who influence business firm directly while general forces include social, political, economic, legal and technological conditions which affect a business firm indirectly.
3. Inter-relatedness: All the forces/factors of a business environment are closely interrelated. For example, increased awareness of health care has raised the demand for organic food and roasted snacks.
4. Dynamic: Business environment is dynamic in nature which keeps on changing with the change in technology, consumer’s fashion and tastes etc.
5. Uncertainty: Business environment is uncertain as it is difficult to predict the future environmental changes and their impact with full accuracy.
6. Complexity: Business environment is complex which is easy to understand in parts separately but it is difficult to understand in totality.
7. Relativity: Business environment is a relative concept whose impact differs from country to country, region to region and firm to firm. For example, a shift of preference from soft drinks to juices will be welcomed as an opportunity by juice making companies while a threat to soft drink manufacturers.
IMPORTANCE OF BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
1. Identification of opportunities to get first mover advantage: Understanding of business environment helps an organization in identifying advantageous opportunities and getting their benefits prior to competitors, thus reaping the benefits of being a pioneer.
2. Identification of threats: Correct knowledge of business environment helps an organization to identify those threats which may adversely affect its operations. For example, Bajaj Auto made considerable improvements in its two wheelers when Honda & other companies entered the auto industry.
3. Tapping useful resources: Business environment makes available various resources such as capital, labour, machines, raw material etc. toa business firm. In order to know the availability of resources and making them available on time at economical price, knowledge of business environment is necessary.
4. Coping with Rapid changes: Continuous study/scanning of business environment helps in knowing the changes which are taking place and thus they can be faced effectively.
5. Assistance in planning and policy formulation: Understanding and analysis of business environment helps an organization in planning &policy formulation. For example, ITC Hotels planned new hotels in India after observing boom in tourism sector.
Helps in Improving performance: Correct analysis and continuous monitoring of business environment helps an organization in improving its performance.
Economic Environment in India
As a part of economic reforms, the Government of India announced New Economic Policy in July 1991 for taking out the country out of economic difficulty and speeding up the development of the country.
Main features of NEP, 1991 are as follows:
1. Only six industries were kept under licensing scheme.
2. The role of public sector was limited only to four industries.
3. Disinvestment was carried out in many public sector enterprises.
4. Foreign capital/investment policy was liberalized and in many sectors100% direct foreign investment was allowed.
5. Automatic permission was given for signing technology agreements with foreign companies.
6. Foreign investment promotion board (FIPB) was setup to promote & bring foreign investment in India.
7. Various benefits were offered to small scale industries.
The three main strategies adopted for the above may be defined as follows:
1. Globalisation:
• Integrating the economy of a country with the economies of other countries to facilitate freer flow of trade, capital, persons and technology across borders. It leads to the emergence of a cohesive global economy.
• Till 1991, the Government of India had followed a policy of strictly regulating imports in value and volume terms. These regulations were with respect to (a) licensing of imports, (b) tariff restrictions and (c) quantitative restrictions.
• NEP ‘91 advocated rapid advancement in technology and directed trade liberalization towards:
a. Import Liberalisation
b. Export promotion towards rationalization of the tariff structure and
c. Reforms w.r.t foreign exchange
2. Liberalisation:
= Liberalising the Indian business and industry from all unnecessary controls and restrictions. That is relaxing rules and regulations which restrict the growth of the private sector and allowing the private sector to take part in economic activities that were earlier reserved for the government sector. The steps taken for this were:
a. Abolishing licensing b. Freedom in deciding the scale of operations c. Removal of restrictions on movement of goods and services. d. Freedom in fixing prices.
e. Reduction in tax rates and unnecessary controls f. Simplifying procedures for import and exports g. Making it easy to attract foreign capital.
3. Privatization:
• Refers to the reduction of the role of the public sector in the economy of a country.
• Transfer of ownership and control from the private to the public sector (disinvestment) can be done by : a. Sale of all/some asses of the public sector enterprises. b. Leasing of public enterprises to the private sector. c. Transfer of management of the public enterprise to the private sector.
• To achieve privatization in India, the government redefined the role of the public sector and -
a. Adopted a policy of planned disinvestment of the public sector
b. Refer the loss making and sick units to the Board of Industrial and Financial Reconstruction (BIFR)
DIMENSIONS/COMPONENTS OF BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
1. Economic Environment: It has immediate and direct economic impact on a business. Rate of interest, inflation rate, change in the income of people, monetary policy, price level etc. are some economic factors which could affect business firms. Economic environment may offer opportunities to a firm or it may put constraints.
2. Social Environment: It includes various social forces such as customs, beliefs, literacy rate, educational levels, lifestyle, values etc. Changes in social environment affect an organization in the long run. Example: Now a days people are paying more attention towards their health, as a result of which demand for mineral water, diet coke etc. has increased while demand of tobacco, fatty food products has decreased.
3. Technological Environment: It provides new and advance ways/techniques of production. A businessman must closely monitor the technological changes taking place in the industry as it helps in facing competition and improving quality of the product. For Example, Digital watches in place of traditional watches, artificial fabrics in place of traditional cotton and silk fabrics, booking of railway tickets on internet etc.
4. Political Environment: Changes in political situation also affect business organizations. Political stability builds confidence among business community while political instability and bad law & order situation may bring uncertainty in business activities. Ideology of the political party, attitude of government towards business, type of government-single party or coalition government affects the business Example: Bangalore and Hyderabad have become the most popular locations for IT due to supportive political climate.
5. Legal Environment: It constitutes the laws and legislations passed by the Government, administrative orders, court judgements, decisions of various commissions and agencies. Businessmen have to act according to various legislations and their knowledge is very necessary. Example: Advertisement of Alcoholic products is prohibited and it is compulsory to give statutory warning on advertisement of cigarettes.
MAJOR STEPS IN ECONOMIC FORMS
1. New Industrial Policy - Under this the industries have been freed to a large extend from licences and other controls. Efforts have been made to encourage foreign investment.
2. New Trade Policy - The Foreign trade has been freed from the unnecessary control. The age old restrictions have been eliminated.
3. Fiscal Reforms. The greatest problem confronting the Indian Govt. is excessive fiscal deficit.
(a) Fiscal Deficit - It means country is spending more than its income
(b) Gross Domestic Product (GDP) - It is the sum total of the financial value of all goods & services produced in a year in a country.
4. Monetary Reform - It is a sort of control policy through which the central bank controls the supply of money with a view to achieving objectives of general economic policy.
5. Capital Market Reforms- The Govt. has taken the following steps for the development of this market:
(1) SEBI has been established.
(2) The restriction in respect of interest on debentures has been lifted.
(3) Private Sector has been permitted to establish Mutual Fund.
6. Dismantling Price control - The govt. has taken steps to remove price control in many products especially in fertilizers, iron and steel, petro products. Restrictions on the import of these things have also been removed.
IMPACT OF GOVERNMENT POLICY CHANGESON BUSINESS AND INDUSTRY
1. Increasing Competition: De-licencing and entry of foreign firms Indian market is increased the level of competition for Indian firms.
2. More Demanding Customers: Now customers are more aware and they keep maximum information of the market as the result of which now market is customer/buyer oriented, Now, products are produced keeping in mind the demands of the customers.
3. Rapid Changing Technological Environment: Rapid Technological advancement has changed/improved the production process as a result of which maximum production is possible at minimum cost but it leads to tough challenges in front of small firms.
4. Necessity for Change- After New Industrial. Policy the market forces (demand & supply) are changing at a very fast rate. Change in the various components of business environment has made it necessary for the business firms to modify their policies & operations from time to time.
5. Need for Developing Human Resources: The changing market conditions of today requires people with higher competence and greater commitment, hence there is a need for developing human resources which could increase their effectiveness and efficiency.
6. Market Orientation: Earlier selling concept was famous in the market now its place is taken by the marketing concept. Today firms produce those goods & services which are required by the customers. Marketing research, educational advertising, after sales services have become more significant.
7. Reduction in budgetary Support to Public Sector: The budgetary support given by the government to the public sector is reducing thus the public sector has to survive and grow by utilising their own resources efficiently.
