Algebraic Expressions - Revision Notes
CBSE Class–VII Subject Mathematics
Revision Notes
Chapter –12
Algebraic Expressions
Algebraic expressions are formed from variables and constants. We use the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division on the variables and constants to form expressions. For example, the expression
4xy + 7 is formed from the variables x and y and constants 4 and 7. The constant 4 and the variables x and y are multiplied to give the product 4xy and the constant 7 is added to this product to give the expression.- Variable: Symbols which are used to represent or replace numbers. They are denoted as x, y, z, a, b, c…… and can take different numerical values. We generally use small letters to represent variables.
- Constant: A symbol having a fixed numerical value. Example: 2, -10, etc.
- Expressions are made up of terms. Terms are added to make an expression. For example, the addition of the terms 4xy and 7 gives the expression 4xy + 7.
- A term is a product of factors. The term 4xy in the expression 4xy + 7 is a product of factors x, y and 4. Factors containing variables are said to be algebraic factors.
- The coefficient is the numerical factor in the term. Sometimes anyone factor in a term is called the coefficient of the remaining part of the term.
- Any expression with one or more terms is called a polynomial.
- Specifically a one term expression is called a monomial.
- A two-term expression is called a binomial.
- A three-term expression is called a trinomial.
- Terms which have the same algebraic factors are liketerms. Terms which have different algebraic factors are unlike terms. Thus, terms 4xy and – 3xy are like terms; but terms 4xy and – 3x are not like terms.
- The sum (or difference) of two like terms is a like term with coefficient equal to the sum (or difference) of the coefficients of the two like terms. Thus,
8xy – 3xy = (8 – 3 )xy, i.e., 5xy. - When we add two algebraic expressions, the like terms are added as given above; the unlike terms are left as they are. Thus, the sum of
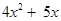 and
and
2x + 3 is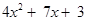 ; the like terms 5x and 2x add to 7x; the unlike terms
; the like terms 5x and 2x add to 7x; the unlike terms 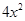 and 3 are left as they are.
and 3 are left as they are. - In situations such as solving an equation and using a formula, we have to find the value of an expression. The value of the expression depends on the value of the variable from which the expression is formed. Thus, the value of 7x – 3 for x = 5 is 32, since 7(5) – 3 = 35 – 3 = 32.
- Rules and formulas in mathematics are written in a concise and general form using algebraic expressions: Thus, the area of rectangle = lb, where l is the length and b is the breadth of the rectangle.
- The general (nth) term of a number pattern (or a sequence) is an expression in n.
- Thus, the nth term of the number pattern 11, 21, 31, 41, . . . is (10n + 1).
