Understanding Quadrilaterals - Solutions 3
CBSE Class –VIII Mathematics
NCERT Solutions
CHAPTER - 3
Understanding Quadrilaterals (Ex. 3.3)
NCERT Solutions
CHAPTER - 3
Understanding Quadrilaterals (Ex. 3.3)
1. Given a parallelogram ABCD. Complete each statement along with the definition or property used.
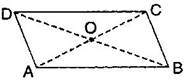
(i) AD = _______________
(ii)  DCB = ______________
DCB = ______________
 DCB = ______________
DCB = ______________
(iii) OC = _____________
(iv) 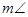 DAB +
DAB + 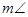 CDA = ________
CDA = ________
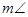 DAB +
DAB + 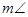 CDA = ________
CDA = ________
Ans. (i) AD = BC
[Since opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal]
(ii)  DCB =
DCB =  DAB
DAB
 DCB =
DCB =  DAB
DAB
[Since opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal]
(iii) OC = OA
[Since diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other]
(iv) 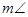 DAB +
DAB + 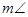 CDA =
CDA = 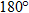
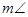 DAB +
DAB + 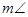 CDA =
CDA = 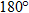
[Adjacent angles in a parallelogram are supplementary]
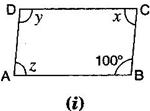
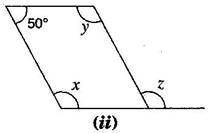
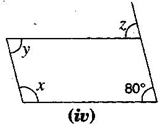
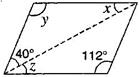
2. Consider the following parallelograms. Find the values of the unknowns 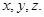
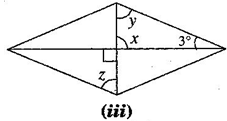





Note: For getting correct answer, read 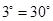 in figure (iii)
in figure (iii)
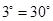 in figure (iii)
in figure (iii)
Ans. (i)  B +
B +  C =
C = 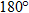
 B +
B +  C =
C = 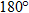
[Adjacent angles in a parallelogram are supplementary]


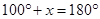


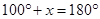

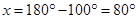
And 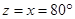
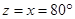
[Since opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal]
Also 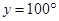
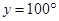
[Since opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal]
(ii) 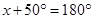
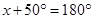
[Adjacent angles in a 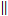 gm are supplementary]
gm are supplementary]
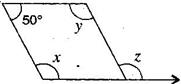

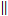 gm are supplementary]
gm are supplementary]

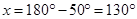

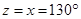
[Corresponding angles]
 y = x = 130 degrees
y = x = 130 degrees
[Since opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal]
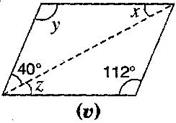
(iii) 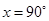
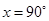
[Vertically opposite angles]
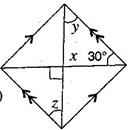

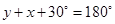


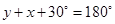
[Angle sum property of a triangle]

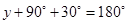

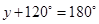

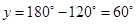

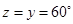
[Alternate angles]
(iv) 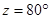
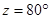
[Corresponding angles]

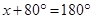
[Adjacent angles in a 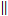 gm are supplementary]
gm are supplementary]


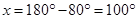
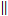 gm are supplementary]
gm are supplementary]

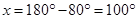
And 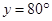
[Opposite angles are equal in a  gm]
gm]
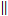 gm]
gm]
(v) 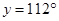
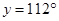
[Opposite angles are equal in a 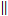 gm]
gm]

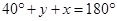
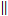 gm]
gm]

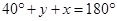
[Angle sum property of a triangle]

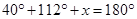

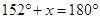

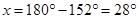
And 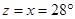
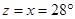
[Alternate angles]
3. Can a quadrilateral ABCD be a parallelogram, if:
(i)  D +
D +  B =
B = 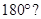
 D +
D +  B =
B = 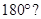
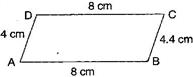
(ii) AB = DC = 8 cm, AD = 4 cm and BC = 4.4 cm?
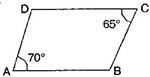
(iii)  A =
A = 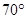 and
and  C =
C = 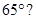
 A =
A = 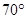 and
and  C =
C = 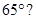
Ans. (i)  D +
D +  B =
B = 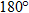
 D +
D +  B =
B = 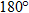
It can be, but here, it needs to be a square or a rectangle.

(ii) No, in this case, because one pair of opposite sides are equal and another pair of opposite sides are unequal. So, it is not a parallelogram.
(iii) No. A
A 
 C.
C.

(ii) No, in this case, because one pair of opposite sides are equal and another pair of opposite sides are unequal. So, it is not a parallelogram.

(iii) No.
 A
A 
 C.
C.
Since opposite angles are equal in parallelogram and here opposite angles are not equal in quadrilateral ABCD. Therefore it is not a parallelogram.

4. Draw a rough figure of a quadrilateral that is not a parallelogram but has exactly two opposite angles of equal measures.
Ans. ABCD is a quadrilateral in which angles  A =
A =  C =
C = 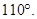
 A =
A =  C =
C = 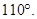
Therefore, it could be a kite.

5. The measure of two adjacent angles of a parallelogram are in the ratio 3 : 2. Find the measure of each of the angles of the parallelogram.
Ans. Let two adjacent angles be 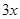 and
and 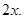
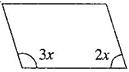
Since the adjacent angles in a parallelogram are supplementary.
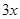 and
and 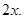

Since the adjacent angles in a parallelogram are supplementary.

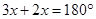

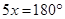

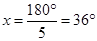
 One angle =
One angle = 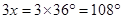
And Another angle = 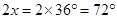
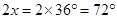
6. Two adjacent angles of a parallelogram have equal measure. Find the measure of the angles of the parallelogram.
Ans. Let each adjacent angle be 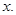
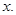
Since the adjacent angles in a parallelogram are supplementary.

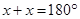

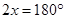

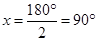
Hence, each adjacent angle is 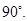
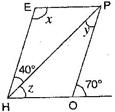
7. The adjacent figure HOPW is a parallelogram. Find the angle measures 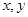 and
and 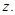 State the properties you use to find them.
State the properties you use to find them.
 HOP +
HOP + 
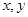 and
and 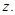 State the properties you use to find them.
State the properties you use to find them.
 HOP +
HOP + 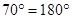
Ans. Here  HOP =
HOP = 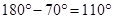
 HOP =
HOP = 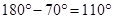
[Angles of linear pair]
And  E =
E =  HOP
HOP
 E =
E =  HOP
HOP
[Opposite angles of a  gm are equal]
gm are equal]
 gm are equal]
gm are equal]
 PHE =
PHE =  HPO
HPO
[Alternate angles]

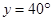
Now  EHO =
EHO =  O =
O = 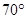
 EHO =
EHO =  O =
O = 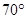
[Corresponding angles]

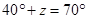

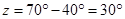
Hence, 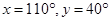 and
and 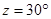
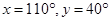 and
and 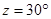
8. The following figures GUNS and RUNS are parallelograms. Find  and
and  (Lengths are in cm)
(Lengths are in cm)
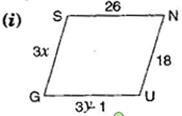
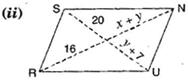
Ans. (i) In parallelogram GUNS,
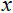 and
and 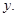 (Lengths are in cm)
(Lengths are in cm)

Ans. (i) In parallelogram GUNS,
GS = UN
[Opposite sides of parallelogram are equal]

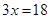

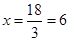 cm
cm
Also GU = SN
[Opposite sides of parallelogram are equal]

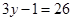

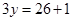

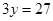

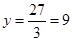 cm
cm
Hence, 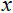 = 6 cm and
= 6 cm and 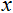 = 9 cm.
= 9 cm.
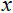 = 6 cm and
= 6 cm and 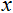 = 9 cm.
= 9 cm.
(ii) In parallelogram RUNS,
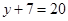
[Diagonals of  gm bisects each other]
gm bisects each other]
 gm bisects each other]
gm bisects each other]
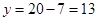 cm
cm
And 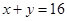
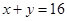

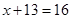

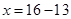

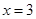 cm
cm
Hence, 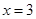 cm and
cm and 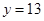 cm.
cm.
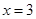 cm and
cm and 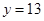 cm.
cm.
9. In the figure, both RISK and CLUE are parallelograms. Find the value of 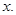
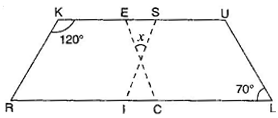
Ans. In parallelogram RISK,
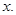

Ans. In parallelogram RISK,
 RIS =
RIS =  K =
K = 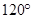
[Opposite angles of a 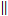 gm are equal]
gm are equal]
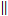 gm are equal]
gm are equal]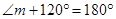 [Linear pair]
[Linear pair]
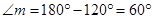
And  ECI =
ECI =  L =
L = 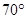
 ECI =
ECI =  L =
L = 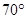
[Corresponding angles]

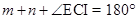
[Angle sum property of a triangle]

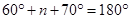

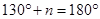

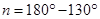 =
= 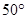
Also 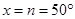
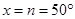
[Vertically opposite angles]
10. Explain how this figure is a trapezium. Which of its two sides are parallel?
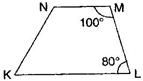
Ans. Here, M +
M +  L =
L = 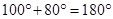

Ans. Here,
 M +
M +  L =
L = 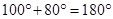
[Sum of interior opposite angles is 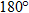 ]
]
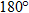 ]
] NM and KL are parallel.
NM and KL are parallel.
Hence, KLMN is a trapezium.
11. Find 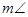 C in figure , if
C in figure , if 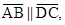
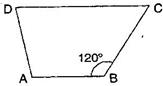
Ans. Here, B +
B +  C =
C = 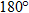
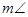 C in figure , if
C in figure , if 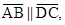

Ans. Here,
 B +
B +  C =
C = 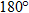
[
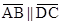 ]
]

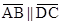 ]
]
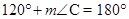

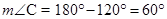
12. Find the measure of  P and
P and  S if
S if 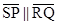 in given figure.
in given figure.
 P and
P and  S if
S if 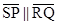 in given figure.
in given figure.
(If you find  R is there more than one method to find
R is there more than one method to find  P)
P)
Ans. Here, P +
P +  Q =
Q = 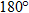
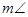 R is there more than one method to find
R is there more than one method to find 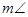 P)
P)
Ans. Here,
 P +
P +  Q =
Q = 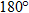
[Sum of co-interior angles is 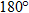 ]
]
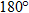 ]
]
 P +
P + 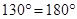

 P =
P = 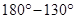

 P =
P = 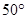

 R =
R = 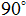 [Given]
[Given]
 S +
S + 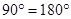

 S =
S = 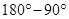

 S =
S = 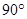
Yes, one more method is there to find  P.
P.
 P.
P. S +
S +  R +
R +  Q +
Q +  P =
P = 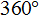
[Angle sum property of quadrilateral]

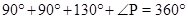

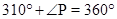

 P =
P = 

 P =
P = 