Understanding Quadrilaterals - Revision Notes
CBSE Class 8 Mathematics
Revision Notes
Chapter – 3
Understanding Quadrilaterals
Revision Notes
Chapter – 3
Understanding Quadrilaterals
- Parallelogram: A quadrilateral with each pair of opposite sides parallel.
(1) Opposite sides are equal.
(2) Opposite angles are equal.
(3) Diagonals bisect one another.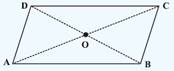
- Rhombus: A parallelogram with sides of equal length.
(1) All the properties of a parallelogram.
(2) Diagonals are perpendicular to each other.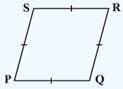
- Rectangle: A parallelogram with a right angle.
(1) All the properties of a parallelogram.
(2) Each of the angles is a right angle.
(3) Diagonals are equal. -

- Square: A rectangle with sides of equal length.
(1) All the properties of a parallelogram, rhombus and a rectangle.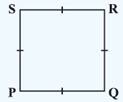
- Kite: A quadrilateral with exactly two pairs of equal consecutive sides
(1) The diagonals are perpendicular to one another
(2) One of the diagonals bisects the other.
(3) In the figure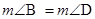 but
but 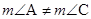 .
.
- Trapezium: A quadrilateral having exactly one pair of parallel sides.
- Diagonal: A simple closed curve made up of only line segments. A line segment connecting two non-consecutive vertices of a polygon is called diagonal.

- Convex : The measure of each angle is less than
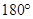 .
. - Concave: The measure of at least one angle is more than
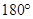
- Quadrilateral: Polygon having four sides.
- Element of quadrilateral:
(i) Sides: Line segments joining the points.
(ii) Vertices: Point of intersection of two consecutive sides.
(iii) Opposite sides: Two sides of a quadrilateral having no common end point.
(iv) Opposite Angles: Two angles of a quadrilateral not having a common arm.
(v) Diagonals: Line segment obtained by joining the opposite vertices.
(vi) Adjacent Angles: Two angles of a quadrilateral having a common arm.
(vii) Adjacent Sides: Two sides of a quadrilateral having a common end point.
