Forms of Market - Solutions
CBSE Class 11 Economics
NCERT Solutions
Chapter-04 (Microeconomics)
Theory of the Firm Under Perfect Competition
1. What are the characteristics of a perfectly competitive market?
Ans: Perfect Competition: It is a market wherein there are large number of buyers and sellers of homogeneous product and the price of the product is determined by the industry. There is one price that prevails in the market and all the firms sell the product at the prevailing price.
Features of Perfectly Competitive Market
- Free and Perfect Competition: In a perfect market, there are no checks either on the buyers or sellers. They are free to buy or to sell to any person. It means there are no monopolies.
- Cheap and Efficient Transport and Communication: Uniform price for the commodity would not be possible if the changes in the prices are not quickly adjusted or the commodity cannot be quickly transported. Thus cheap and efficient means of transport and communication are must.
- Wide Extent: Sometimes wide market is regarded as the same thing as the perfect market. For wide market, the commodity should have permanent and universal demand. The commodity should be portable. Means of transport and communication should be quick. There should be peace and security and extensive division of labour.
- Large number of firms: In this market, a product is produced and sold by large number of firms. Since there are large number of firms, therefore each firm is supplying only a small part of the total supply in the market, thus no one firm has any market power. It implies that no firm can influence the price of the product rather each must accept the price set by the forces of market demand and supply. The firms are price-takers instead of price-makers.
- Large number of buyers: In a perfectly competitive market, there are large numbers of buyers each demanding a small part of the total market supply of the product. As a result, no single buyer is in a position to influence the market price determined by the forces of market demand and supply.
- Homogeneous Product: In a perfectly competitive market, all the firms produce and supply the identical products. It means that the products of all the firms are perfect substitutes of each other. As a result of this, the price elasticity of demand for a firm’s product is infinite.
- Free entry and exit: In a perfectly competitive market, there are no restrictions on the entry of new firms into market or on the exit of existing firms from the market.
- Perfect knowledge: In a perfectly competitive market, the firms and the buyers possess perfect information about the market. It implies that no buyer or firm is ignorant about the price prevailing in the market.
- Perfect mobility of factors of production: In a perfectly competitive market, the factors of production are completely mobile leading to factor-price equalization throughout the market.
2. How are the total revenue of a firm, market price, and the quantity sold by that firm related to each other?
Ans: Total revenue is defined as the total sales proceeds of a producer by selling corresponding level of output. In other words, it is defined as price times the quantity of output sold.
Total Revenue = Price x Quantity of output sold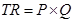
TR = PQ
In a perfectly competitive market, the market price is given, i.e., a firm act as a price taker and cannot influence the price. Hence, a particular firm can influence its TR by altering the quantity of output sold.
3. What is the price line?
Ans: Price line is the graphical representation of the relationship between output and price, with x-axis denoting the output and y-axis denoting the price. For a perfectly competitive firm, price line and demand curve are the same.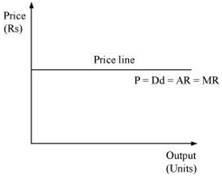
4. Why is the total revenue curve of a price-taking firm an upward-sloping straight line? Why does the curve pass through the origin?
Ans: The total revenue curve for a firm in a perfectly competitive market is an upward sloping curve because the price or AR remains constant and MR is also equal to AR. Thus, TR can only be influenced by altering the output sold, as the price remains constant. The increase in TR is in the same proportion as the increase in the output sold.
The curve passes through the origin, which implies that no matter what the price level is, if the output sold is zero, TR will also be zero.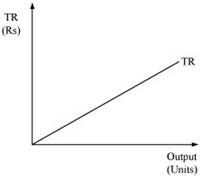
5. What is the relation between market price and average revenue of a price taking firm?
Ans: Average Revenue is defined as the revenue per unit of the output sold. It is expressed as the ratio between total revenue and the output sold.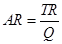
We know that,
TR = P × Q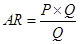
AR = P
Thus, the market price and the average revenue are the same for a perfect competitive firm.
6. What is the relation between market price and marginal revenue of a price-taking firm?
Ans: Marginal revenue is defined as the change in the total revenue that occurs due to the sale of one more unit of output. It is calculated as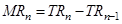
Where,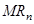 = Marginal revenue due to nth unit of output
= Marginal revenue due to nth unit of output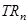 = Total revenue due to n units of output
= Total revenue due to n units of output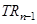 = Total revenue due to (n - 1) units of output
= Total revenue due to (n - 1) units of output
Suppose that the market price is P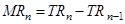
= 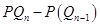
MR = 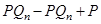
MR = P. Thus, for a perfect competitive firm, marginal revenue is equal to the market price per unit of output.
7. What conditions must hold if a profit-maximizing firm produces positive output in a competitive market?
Ans: The following three conditions must hold if a profit maximizing firm produces positive level of output (say equilibrium output Q*) in a competitive market:
i) MR must be equal to MC at Q*.
ii) MC should be upward sloping or rising at Q*.
iii) In short run - Price must be greater than or equal to AVC. i.e. 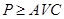 at Q*.
at Q*.
In long run - Price must be greater than or equal to LAC.
8. Can there be a positive level of output that a profit-maximizing firm produces in a competitive market at which market price is not equal to marginal cost? Give an explanation.
Ans: There cannot be any positive level of output that a firm produce at which price is not equal to MC. Let us evaluate the following two cases where price is not equal to MC.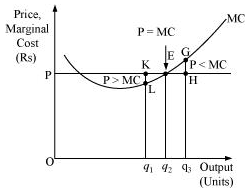
Case A: If P > MC
At output 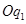 , Price is
, Price is 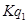 , while the MC is
, while the MC is 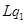 . So,
. So, 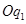 is not the profit maximising output. This is due to the fact that the firm can increase its profit level by expanding its output to
is not the profit maximising output. This is due to the fact that the firm can increase its profit level by expanding its output to 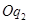 .
.
Case B: If P < MC
At output 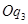 , price is
, price is 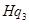 and MC is
and MC is 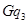 . So,
. So, 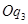 is not the profit maximising output. This is because the firm can increase its profit by reducing its output level to
is not the profit maximising output. This is because the firm can increase its profit by reducing its output level to 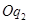 .
.
Thus, at profit maximising point, price must be equal to MC and it cannot be greater or lesser than MC.
9. Will a profit-maximising firm in a competitive market ever produce a positive level of output in the range where the marginal cost is falling? Give an explanation.
Ans: It is not possible for any perfect competitive firm to produce a positive level of output in a range where MC is falling. This is because, according to one of the conditions of profit-maximization, MC curve should be upward sloping or the slope of MC curve should be positive at the equilibrium level of output.
Let us take an example: At point Z price is equal to MC, but MC is falling and is negatively sloped. For any level of output more than 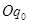 , the firm is facing price > MC, which implies that the profit can be maximized by increasing the output level further.
, the firm is facing price > MC, which implies that the profit can be maximized by increasing the output level further.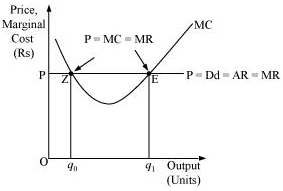
Hence, the point 'E' is the equilibrium point, where a profit maximising firm would operate and produce 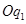 units of output and its profit will be maximized.
units of output and its profit will be maximized.
10. Will a profit-maximising firm in a competitive market produce a positive level of output in the short run if the market price is less than the minimum of AVC?
Ans: It is not possible for a firm to produce positive level of output in the short run if the price is less than the minimum of AVC. This is because as soon as the market price falls below the minimum of SAVC, which implies that the firm is not able to cover its fixed as well as variable costs, and thus it will stop production.
Let us understand this concept by taking an example: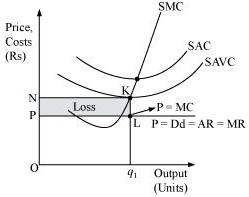
At the point K, price charged by the firm is ON and output sold is Oq1, and the firm generates TR.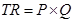
= 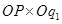
= area (rectangle Oq1LP)
And incurs the variable cost of TVC
TVC = SAVC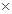 Quantity of output
Quantity of output
= 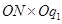
= area (rectangle 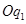 KN)
KN)
Profit earned by the firm = TR - TC = TR - (TVC + TFC)
= TR - TVC – TFC
If the firm is not producing anything then at zero level of output, the firm's TR and TVC will be zero. However, the firm has to bear TFC. Thus at zero level of output, the profit earned by the firm is
Profit = 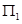 = TR - TVC – TFC
= TR - TVC – TFC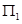 = -TFC
= -TFC
Now if it produces 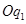 level of output, then the profit earned will be
level of output, then the profit earned will be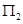 = TR - TVC – TFC
= TR - TVC – TFC
= area (rectangle Oq1LP) - area (rectangle Oq1KN) – TFC
Or, 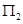 = -area (rectangle PLKN) – TFC
= -area (rectangle PLKN) – TFC
This implies that 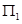 is greater than
is greater than 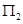 . The firm incurs more loss if it produces
. The firm incurs more loss if it produces 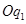 level of output than the loss associated with zero level of output. Thus the firm will stop production whenever P < SAVC and therefore at profit maximising level of output, the price must be greater than or equal to SAVC in the short run.
level of output than the loss associated with zero level of output. Thus the firm will stop production whenever P < SAVC and therefore at profit maximising level of output, the price must be greater than or equal to SAVC in the short run.
11. Will a profit-maximising firm in a competitive market produce a positive level of output in the long run if the market price is less than the minimum of AC? Give an explanation.
Ans: It is not possible for a firm to produce positive level of output in the long run if the market price falls short of the minimum of AC. This is because, in the long run there is free entry and exit of firms and all firms earn normal profit. Therefore, any firm making losses in long run will stop production.
Let us understand this concept through an example: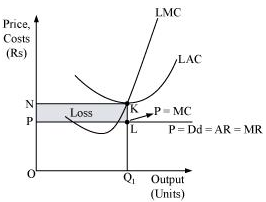
At Oq1 level of output,
Price charged by the firm = OP.
Revenue generated by the firm (TR) = 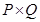
= 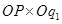
= area (rectangle 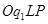 )
)
Cost of producing Oq1 level of output (TC) = LAC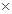 Quantity of output
Quantity of output
= 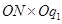
TC = area (rectangle 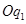 KN)
KN)
Profit earned by the firm = TR – TC
= area (rectangle 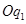 LP) - area (rectangle
LP) - area (rectangle 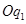 KN)
KN)
= - area (rectangle NKLP)
Thus, the loss incurred by the firm is equal to the area of the rectangle NKLP.
In the long run, all firms earn zero economic profit, and if any firm earns loss or negative profit, then the firm will shut down its production. Thus, if the firm earns loss, i.e. if price is lesser than LAC at any level of output, it will not be the profit maximising output level of the firm.
12. What is the supply curve of a firm in the short run?
Ans: The short run supply curve of perfect competitive firm is the summation of the upward sloping portion of SMC (above the minimum point of SAVC), when price 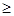 min SAVC, and vertical portion of price-axis, when price < min SAVC.
min SAVC, and vertical portion of price-axis, when price < min SAVC.
Stage 1
When the price is greater than or equal to minimum of SAVC, i.e., P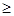 min SAVC.
min SAVC.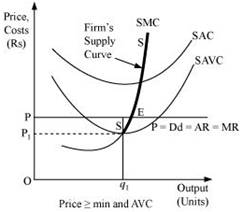
At the market price OP, the three following conditions for equilibrium are fulfilled:
MC = MR
MC is upward sloping
Price exceeds the minimum of SAVC
At this market price the firm is producing profit maximizing output 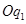 .
.
In this case, the supply curve of the firm is regarded as the upward sloping part of SMC (above the minimum point of SAVC), i.e. SS. When the price is greater than or equal to minimum of SAVC, the supply curve is indicated by SS.
Stage 2
When the price is less than the minimum of SAVC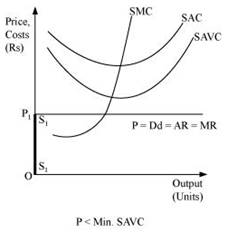
Let us suppose that the firm is facing price 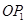 that is lesser than the minimum of SAVC. At this price, the firm cannot continue production as it cannot even cover up its variable costs and thereby incurs losses, which implies that the firm would produce nothing. Thus, it will incur loss that will be equivalent to its fixed costs. It will be lesser compared to the losses associated with producing any positive output level. Thus, the firm will not produce anything at this price and thereby the quantity supplied will be zero. The firm's supply curve is indicated by the darkened vertical line
that is lesser than the minimum of SAVC. At this price, the firm cannot continue production as it cannot even cover up its variable costs and thereby incurs losses, which implies that the firm would produce nothing. Thus, it will incur loss that will be equivalent to its fixed costs. It will be lesser compared to the losses associated with producing any positive output level. Thus, the firm will not produce anything at this price and thereby the quantity supplied will be zero. The firm's supply curve is indicated by the darkened vertical line 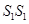 .
.
Therefore, the short run supply curve of perfect competitive firm is (SS +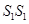 ).
).
13. What is the supply curve of a firm in the long run?
Ans: In the long run, as there is no fixed cost, the perfectly competitive firm's supply curve will be the summation of the upward sloping portion of SMC above the minimum point of LAC (when price 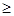 minimum LAC), and the vertical portion of the price axis (when price < minimum of LAC). The long run supply curve of a perfect competitive firm is derived in two stages.
minimum LAC), and the vertical portion of the price axis (when price < minimum of LAC). The long run supply curve of a perfect competitive firm is derived in two stages.
- When price is equal to the minimum of LAC: Let us suppose that the firm is facing market price OP that exceeds the minimum of LAC. MC is equal to MR (at point E) and MC is positively sloped at this point of intersection. Also, the price is greater than the minimum of LAC. Thus, the firm is at long run equilibrium, facing the price OP and producing Oq1 units of output. The supply curve is 'SS', represented by the upward portion of LMC above the minimum of LAC.
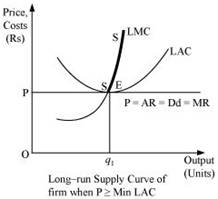
- When the price is less than the minimum of LAC: Let us suppose that the market price faced by a firm is OP1, which is less than the minimum of LAC. At this price, the firm would not produce any output because producing any output will lead the firm to incur losses. Therefore, the firm would not produce anything. So, the supply curve of the firm in the long run for the price less than the minimum of LAC is given by S1S1 and is represented by the darkened vertical part of the price axis.
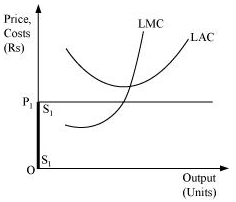
Combining 1st and 2nd stages, the firm's long run supply curve under perfect competition is given by ( + SS).
+ SS).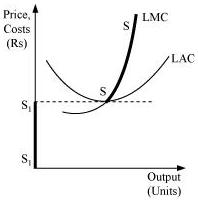
14. How does technological progress affect the supply curve of a firm?
Ans: The supply curve of a firm is a positive function of a state of technology. That is, if the technology available to the firm appreciates, more amount of output can be produced by the firm with the given levels of capital and labour. Due to such innovations or technological advancements, the firm will experience lower cost of production, which will lead to rightward downward shift of the MC curve. This will further lead to rightward shift of the firm's supply curve. Thus, due to the appreciation and advancement of production techniques, the firm will produce more and more output that will be supplied at a given market price.
15. How does the imposition of a unit tax affect the supply curve of a firm?
Ans: A unit tax is the tax imposed on per unit of the output sold. Due to the imposition of unit tax, the cost of production per unit of output increases, which ultimately increases the marginal cost. Consequently, the LMC curve will shift leftward upward and as the supply curve is a portion of LMC, so the supply curve will also shift leftward upward.
Let us understand the effect of imposition of unit tax through an example.
Suppose that a firm is facing the price 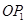 .
. 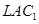 and
and 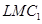 are the long run average cost curve and long run marginal cost curve respectively. Also assume that the government has imposed a unit tax of Rs k per unit of output produced. Now, this will rise the firm's LAC and LMC, as the firm needs to pay Rs k extra on each output produced. Consequently,
are the long run average cost curve and long run marginal cost curve respectively. Also assume that the government has imposed a unit tax of Rs k per unit of output produced. Now, this will rise the firm's LAC and LMC, as the firm needs to pay Rs k extra on each output produced. Consequently,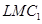 and
and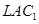 will shift leftward upwards to
will shift leftward upwards to 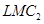 and
and 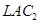 . The magnitude of shift is equal to Rs k. As the supply curve is a part of LMC, it will also shift leftward from
. The magnitude of shift is equal to Rs k. As the supply curve is a part of LMC, it will also shift leftward from 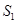 to
to 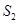 , due to the imposition of the tax. Consequently, the firm will now supply lesser units of output.
, due to the imposition of the tax. Consequently, the firm will now supply lesser units of output.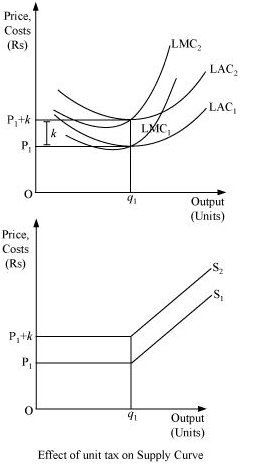
16. How does an increase in the price of an input affect the supply curve of a firm?
Ans: An increase in the price of an input increases the cost of production, which in turn increases the marginal cost of the firm. Consequently, the MC curve will shift upward to the left and the supply curve will also shift leftward upward. Therefore, an increase in the input price negatively affects the supply of the firm.
17. How does an increase in the number of firms in a market affect the market supply curve?
Ans: The market supply curve is a horizontal summation of all the supply curves of individual firms in the market. If the number of firms in a market increases, then the market supply curve will shift rightward as there will be more number of firms supplying more amount of output.
18. What does the price elasticity of supply mean? How do we measure it?
Ans: Price elasticity of supply 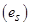 is defined as the degree of the responsiveness of quantity supplied, to the change in the price of a good.
is defined as the degree of the responsiveness of quantity supplied, to the change in the price of a good.
It is expressed as: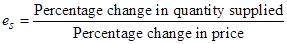
=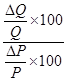
=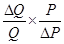
=
Where,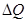 = change in quantity supplied
= change in quantity supplied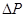 = change in price
= change in price
P = initial price
Q = initial supply
19. Calculate the total revenue, marginal revenue and average revenue schedules in the following table. Market price of each unit of the good is Rs 10.
| Quantity Sold | TR | MR | AR |
| 0 | |||
| 1 | |||
| 2 | |||
| 3 | |||
| 4 | |||
| 5 | |||
| 6 |
Ans:
| Quantity Sold | 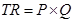 | 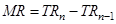 | AR = 10 |
| 0 | - | - | - |
| 1 | 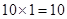 | 10 - 0 = 10 | 10 |
| 2 | 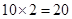 | 20 -10 = 10 | 10 |
| 3 | 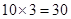 | 30 - 20 = 10 | 10 |
| 4 | 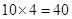 | 40 - 30 = 10 | 10 |
| 5 | 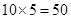 | 50 - 40 = 10 | 10 |
| 6 | 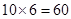 | 60 - 50 = 10 | 10 |
20. The following table shows the total revenue and total cost schedules of a competitive firm. Calculate the profit at each output level. Determine also the market price of the good.
| Quantity Sold | TR | TC | Profit |
| 0 | 0 | 5 | |
| 1 | 5 | 7 | |
| 2 | 10 | 10 | |
| 3 | 15 | 12 | |
| 4 | 20 | 15 | |
| 5 | 25 | 23 | |
| 6 | 30 | 33 | |
| 7 | 35 | 40 |
Ans:
| Quantity Sold | TR | TC | Profit | 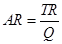 |
| 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 - 5 = -5 | - |
| 1 | 5 | 7 | 5 - 7 = -2 | 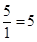 |
| 2 | 10 | 10 | 10 - 10 = 0 | 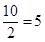 |
| 3 | 15 | 12 | 15 - 12 = 3 | 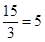 |
| 4 | 20 | 15 | 20 - 15 = 5 | 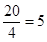 |
| 5 | 25 | 23 | 25 - 23 = 2 | 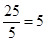 |
| 6 | 30 | 33 | 30 - 33 = 2 | 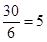 |
| 7 | 35 | 40 | 35 - 40 = -5 | 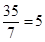 |
