Chemical Effects of Electric Current - Exemplar Solutions 4
NCERT Exemplar Solutions
CHAPTER – 14
Chemical Effects of Electric Current
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
18. An electric current is passed through a conducting solution. List any three possible observations.
Ans: One of the following can be observed when an electric current is passed through a conducting solution:-
- Formation of bubbles of a gas near the electrodes.
- Deposit of a metal on an electrode.
- Change in colour of the solution.
- The solution may become warm. (Any three)
19. In the circuit given as Fig. 14.7, Boojho observed that copper is deposited on the electrode connected to the negative terminal of the battery. Paheli tried to repeat the same experiment. But she could find only one copper plate. Therefore, she took a carbon rod as negative electrode. Will copper be still deposited on the carbon rod? Explain your answer.
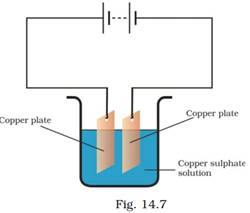
Ans: Yes, a coating of copper will be formed on the carbon rod (electrode connected to the negative terminal of the battery).
When the circuit is complete and the current is flowing, copper sulphate solution will disassociate into copper ions and sulphate ions. Copper ions (positive ions) will get attracted towards the negative electrode and get deposited over the carbon rod. Copper ions from the copper plate connected to the positive terminal will get dissolved into the copper sulphate solution and will replenish the copper ions in the solution.
If required, another copper plate can be used as an anode after the copper plate connected to the positive terminal of the battery wears out. In this way, loss of copper from the copper solution can be restored and the process of electroplating can be continued for the desired time.
This process of depositing a layer of a desired metal (like copper) over another material (like carbon rod), by using the chemical effect of electric current, is known is electroplating.
20. Observe the circuit given in Fig. 14.8.
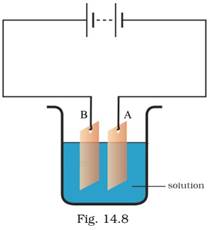
Boojho set up this circuit for purification of copper. What will be the nature of (i) plate A (ii) plate B (iii) the solution? Explain the process of purification.
Ans: After current has been passed in the circuit for some time (around 15 - 20 minutes), the nature of the plates and the solution will be as follows:-
(i) Plate A (Cathode) – Pure copper will be deposited at the cathode and the cathode plate will become thicker due to copper deposit.
(ii) Plate B (Anode) – Impure copper from the anode plate will dissolve into the solution. Anode plate will become thinner due to the erosion and dissolution of copper ions into the cooper sulphate solution.
(iii) The solution – Copper sulphate solution will provide the conducting path for the transfer of copper ions from the impure anode to the pure cathode. The blue colour of the solution will fade after some time.
During the process of purification, copper ions from the impure copper plate (anode) get dissolved into the copper sulphate solution and are transferred to the pure copper plate (cathode). Copper ions get attracted towards the cathode (the negative electrode) and form a layer of deposit.
21. Observe the following circuit given in Fig. 14.9.
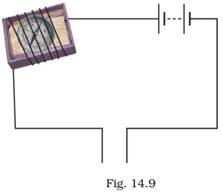
Current does not flow in the circuit if there is a gap between the two wires. Does it indicate that air is a poor conductor of electricity? Does air never conduct electricity? Explain.
Ans: Yes, air is a poor conductor of electricity. When there is a gap between the two wires and the wires do not touch each other, no conduction will happen through the air between the gap. The circuit will not be completed and current will not flow in the circuit.
Air is not a poor conductor under all conditions. Air may conduct electricity under certain conditions such as during a thunderstorm. During a thunderstorm, regions of clouds and air may become electrically charged leading to the formation of lightning.
22. Boojho made the circuit shown in Fig. 14.10. He wanted to observe what happens when an electric current is passed through water. But he forgot to add a few drops of lemon juice to water. Will it make any difference to his observations? Explain.

Ans: If Boojho has used distilled water and forgotten to add lemon juice to the water, the solution in the container will not have any conducting ions and no current will flow through the circuit.
If Boojho has used tap water (that contains mineral salts) instead of distilled water, a feeble current will flow through the circuit. Boojho will observe bubbles of hydrogen gas at the negative electrode (cathode).
23. Observing that the bulb does not glow in the circuit shown in Fig. 14.11 A, Boojho changed the circuit as shown in Fig 14.11 B. He observed deflection in the magnetic compass.
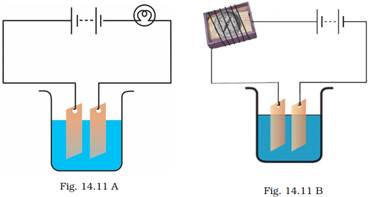
(i) What does the deflection in magnetic compass indicate?
(ii) Why did the bulb not glow in Fig.14.11 A?
(iii) What would be the effect of increase in the number of turns in the coil wound around the magnetic compass in Fig. 14.11 B?
(iv) What will be observed if the number of cells are increased in the circuit shown in Fig. 14.11 B?
Ans: (i) The deflection in magnetic compass needle indicates the presence of a feeble current in the circuit.
(ii) The bulb did not glow in Fig.14.11 A because the current was weak. The magnitude of the current was not sufficient to make the bulb glow.
(iii) If the number of turns in the coil wound around the magnetic compass in Fig. 14.11 B are increased, the magnetic effect of the current will be stronger and the deflection of the magnetic compass will be more.
(iv) If the number of cells in the circuit is increased in the circuit shown in Fig. 14.11 B, the potential difference across the plates will be higher, a stronger current will flow in the circuit and the deflection in the compass will increase further.
24. You are provided with a magnetic compass, an empty match box, a battery of two cells and connecting wires. Using these objects, how will you make a tester for testing a liquid solution? Draw the necessary circuit diagram and explain.
Ans: The following steps should be undertaken for making a tester for testing a liquid solution:-
a) Take the tray from inside the empty match-box.
b) Place a small compass inside the tray.
c) Wrap a connecting wire 5-6 times around the match-box to cover the compass.
d) One end of the connecting wire should be connected to the battery of two cells. The other end of the wire should be left free as shown in the circuit diagram. This end of the wire forms one terminal A of the tester.
e) The other end of the battery should be left free to make the other terminal B of the tester.
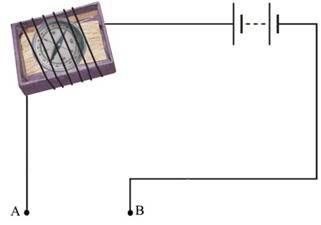
Whenever terminals A and B of the tester are dipped in a conducting solution, the circuit gets completed and a current flows through the circuit of the tester. The needle of the magnetic compass will show a deflection due to the magnetic effect of this current.
The terminals of the tester should be wiped clean before testing another solution.
